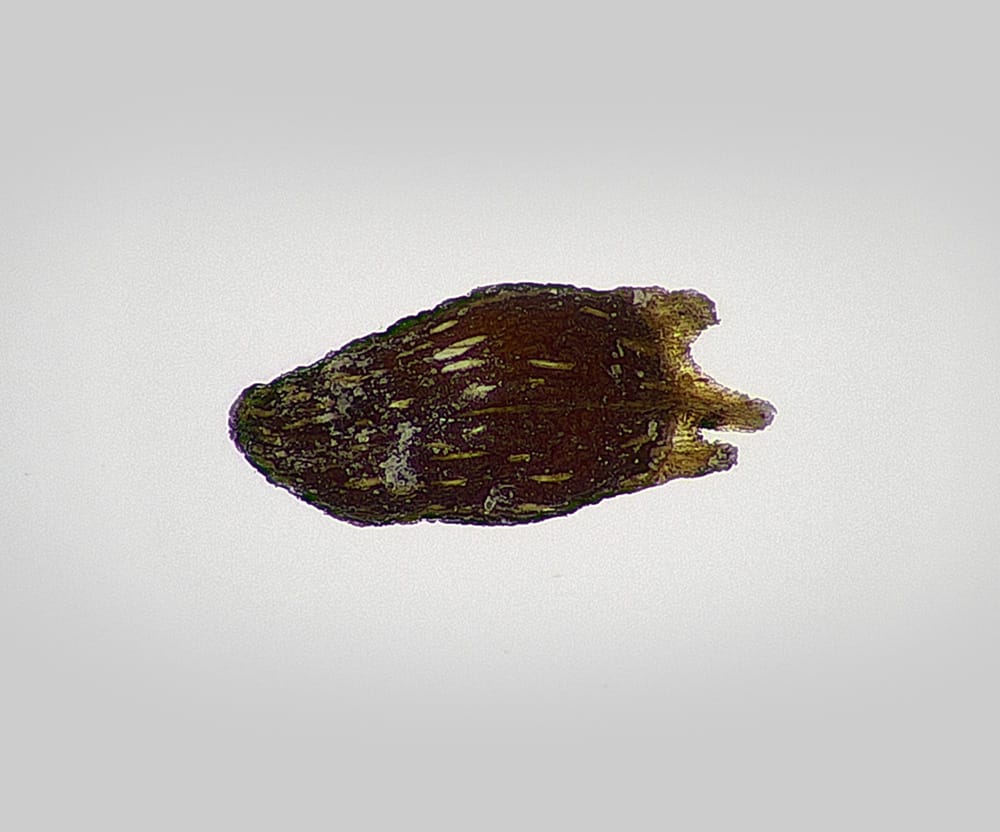
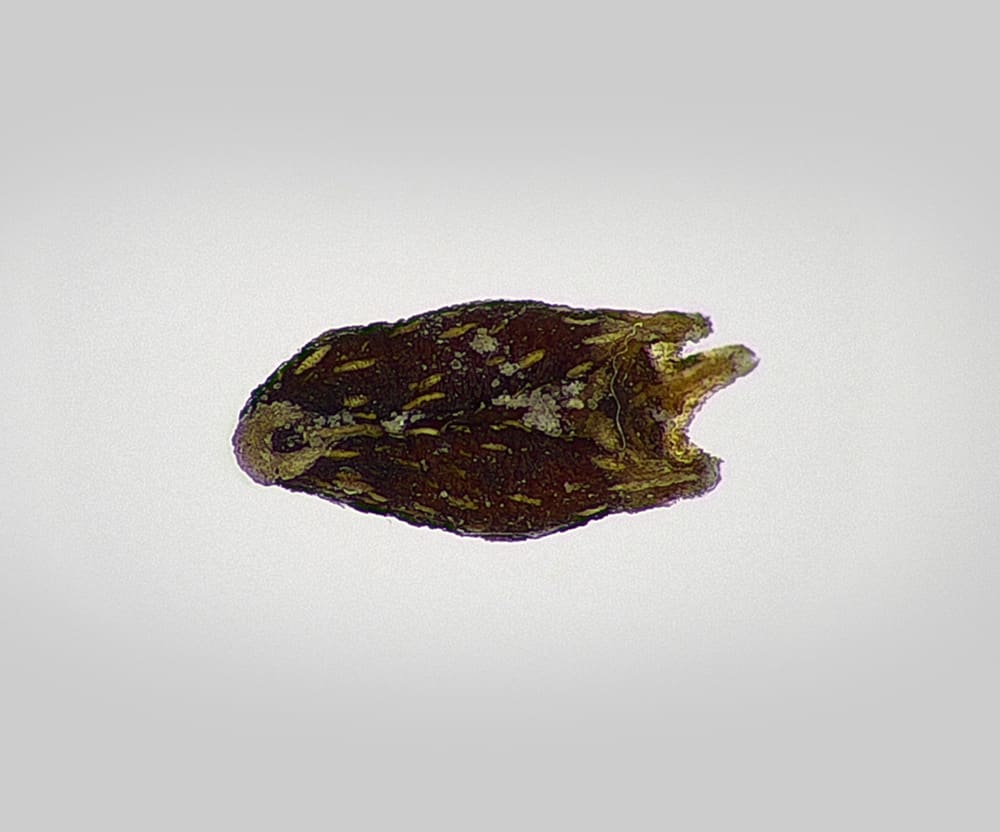
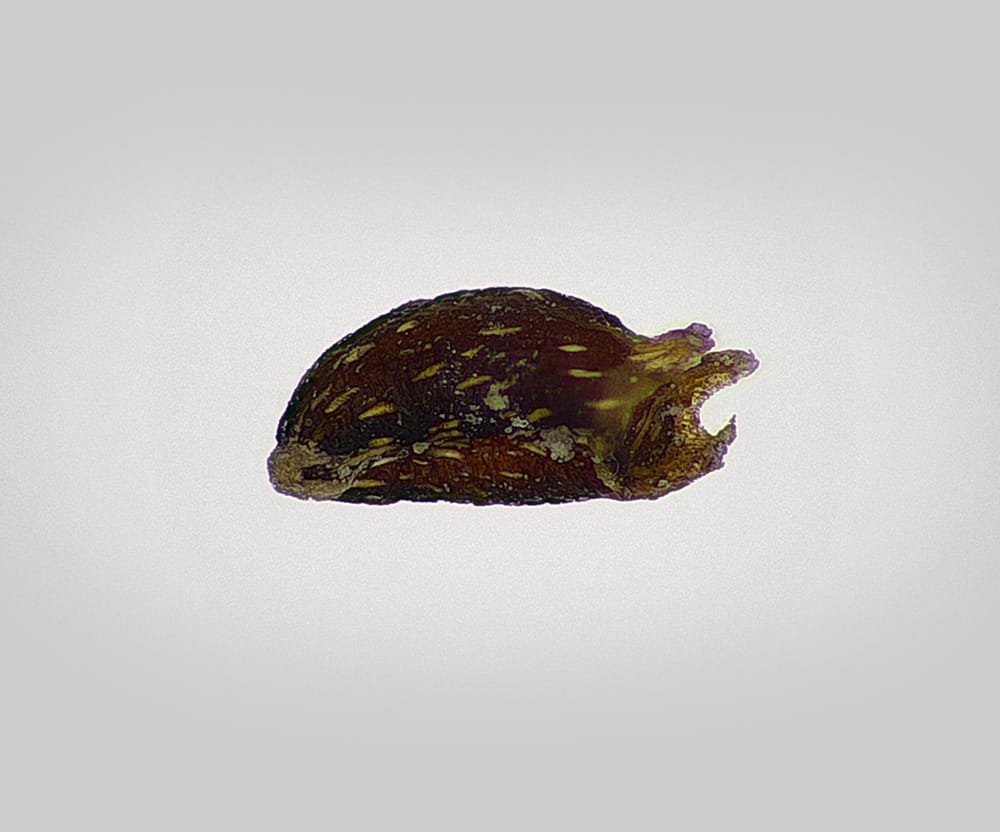
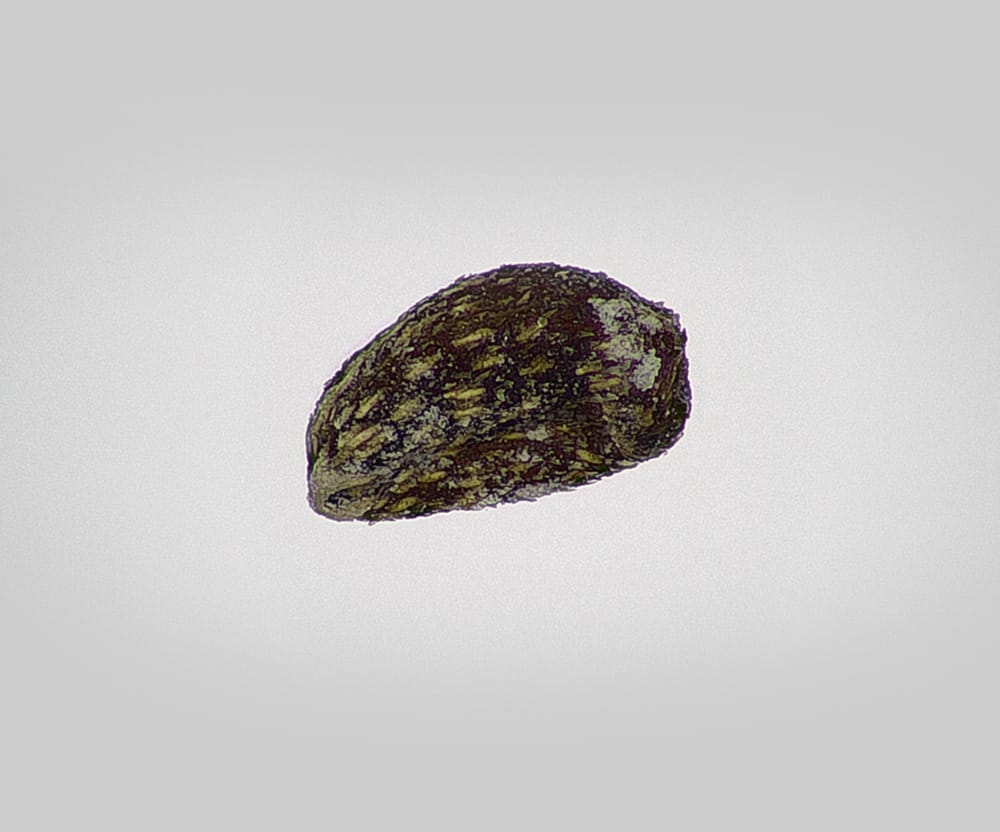
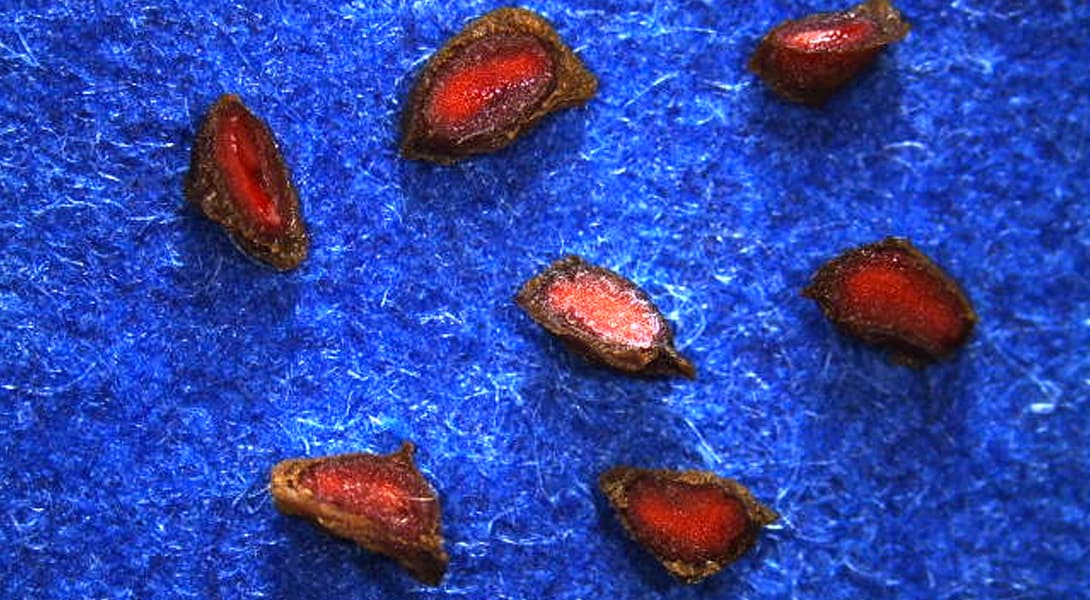
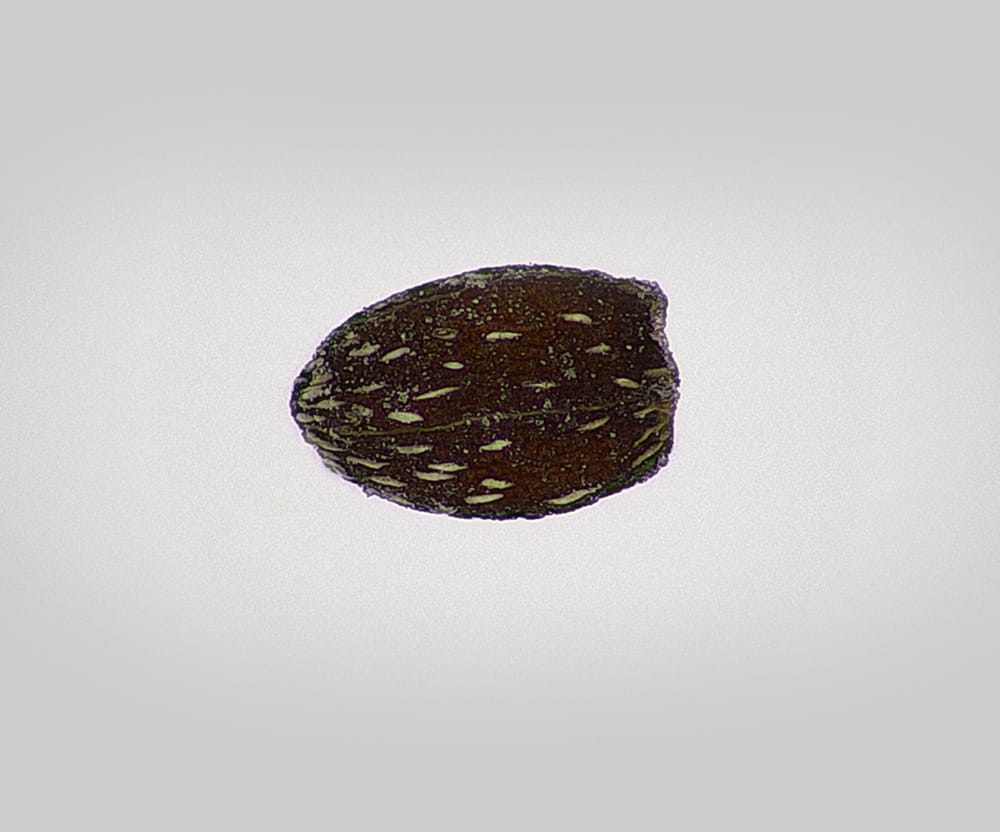
Sherardia arvensis
- Genus
Sherardia
- Family
Rubiaceae
- Synonyms
Read More
Sherardia arvensis var. albiflora
Sherardia arvensis f. argentina
Sherardia arvensis var. hirsute
Sherardia arvensis var. hirta
Sherardia arvensis var. littoralis
Sherardia arvensis var. martima
Sherardia arvensis f. maritima
Sherardia arvensis var. walrawenii
- Common names
Read More
Blue fieldmadder
Blue field-madder
Blue field madder
Field madder
Fieldmadder
Sputwort
See More
Purity
- ISTA PSD
11
See Details - AOSA PSU
2
See Details - Purity working weight (grams)
4
See Details - Other species (OSD)/Noxious working weight (grams)
40
See Details
PSU 2
Seed with at least a portion of the seed coat attached.
Broken seed larger than one-half the original size with at least a portion of the seed coat attached.
Special considerations:
- For Fabaceae: Cotyledons that are broken apart but held together by the seed coat shall be classified as pure seed. Cotyledons that have separated and are not held together by the seed coat are regarded as inert matter irrespective of whether or not the radicle-plumule axis and/or more than half of the seed coat may be attached.
- Wing, when present, is removed and considered inert matter.
- Pericarp (fruit wall), when present on seeds of Desmodium tortuosum, Hedysarum boreale, and Purshia tridentata is removed and considered inert matter.
- Weevil-infested vetch (Vicia spp.) and pea (Pisum sativum) seeds, irrespective of the amount of insect damage, are to be considered pure seed, unless they are broken pieces one-half the original size or less.
- Chalcid-damaged seeds in Fabaceae that are puffy, soft, or dry and crumbly are considered inert matter.
TWS Notes
PSD 11
Seed, provided a portion of the testa is attached.
Piece of seed larger than one-half the original size, provided a portion of the testa is attached.
Fabaceae: cotyledons that are broken apart but held together within the testa.
Seeds and pieces of seed entirely without testa are regarded as inert matter.
Fabaceae: separated cotyledons are regarded as inert matter, irrespective of whether the radicle-plumule axis and/or more than half of the testa is attached.
TWS Notes
Purity working weight (grams)
Noxious working weight/OSD
Germination and dormancy breaking method
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
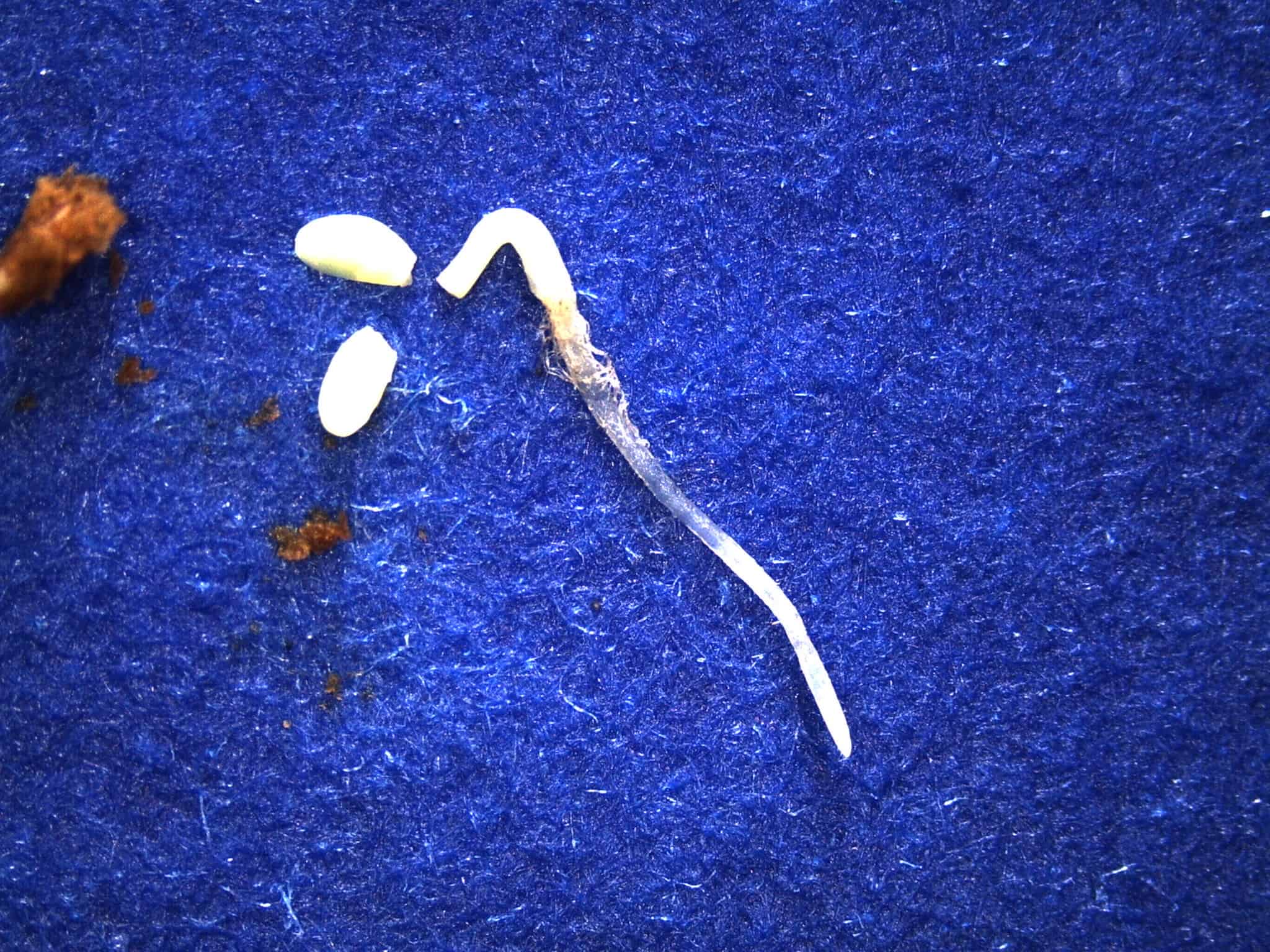
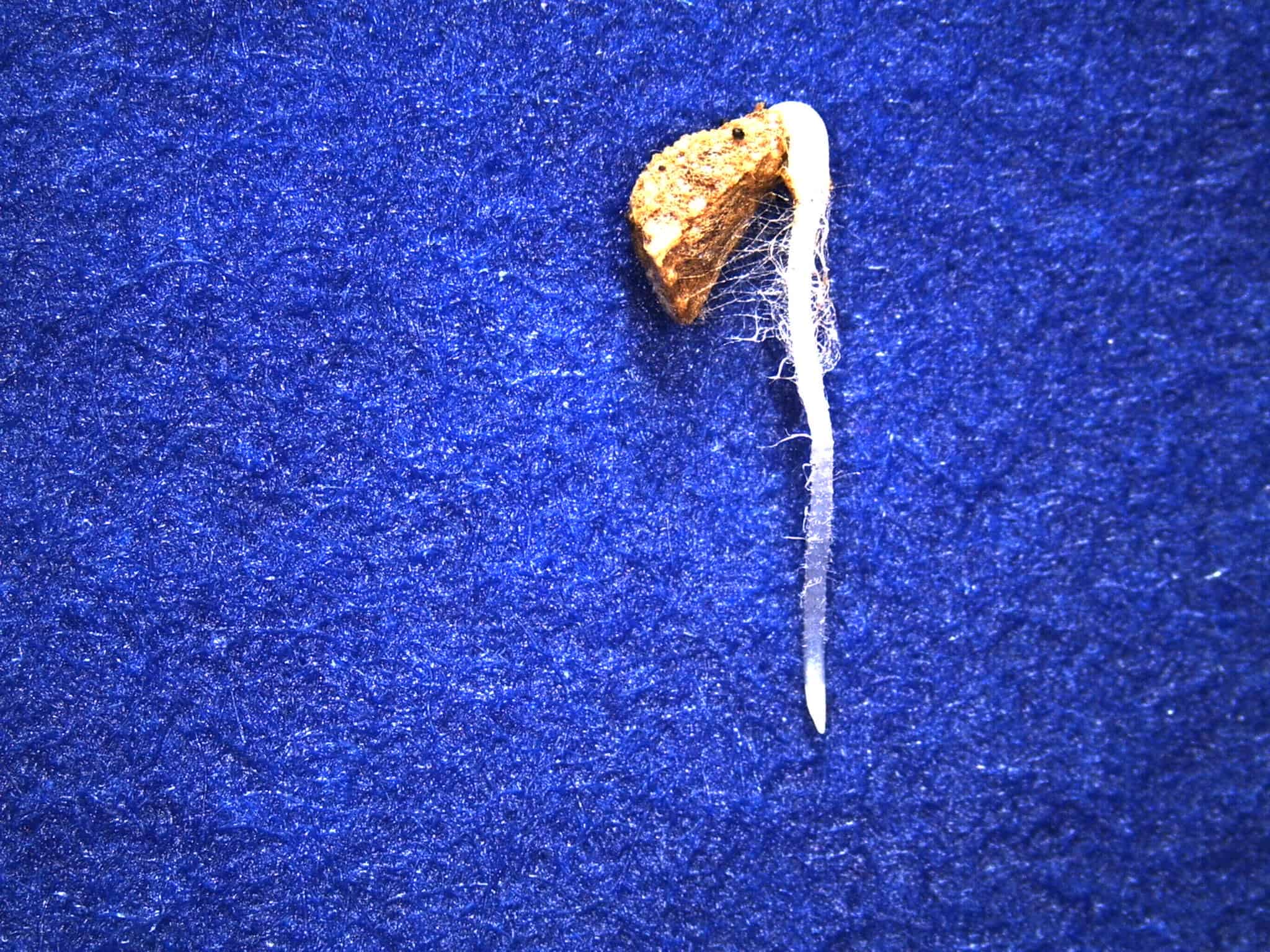
Germination Image Gallery
Description of Normal/Abnormal Seedlings:
Seedlings will be evaluated as normal when they have the essential structures that will have the ability to produce a plant growing in favourable conditions.
Seedling conditions present (singly or in combination), which would cause the seedling to be evaluated as abnormal (not considered viable):
Cotyledons: less than half of the original cotyledon healthy tissue remaining attached.
Epicotyl: missing (considered present if cotyledons are intact).
Hypocotyl: open lesions extending into conducting tissue. Shortened curled or thickened.
Root: None, weak stubby or missing primary root even with weak secondary roots.
Seedling: Albino seedling is abnormal. Primary infection in one or more essential structures. Consider infection to be secondary if seedling is well developed and normally balanced (Normal).
Modified Germination:
Test can be terminated at 14 days if the dormancy is checked with tetrazolium at the termination of the germination test.
Tetrazolium (TZ) Methodology Recommendations:
- Imbibition method and time
Imbibe overnight between moist media or immersed in water
- Option(s) to prepare and cut seed for staining
Cut seed in half longitudinally and place best half face down on filter paper or creped paper moistened with tetrazolium
- Percentage (%) of TZ solution
1.0
- Time and temp of staining (hr)
4 hours up to overnight if needed
- List of important seed structures requiring staining: Entire embryo shall stain red completely. At least a two-thirds of the cotyledon shall stain red.