A
-
Abnormal seedling
- Abnormal seedling. A seedling that does not have all the essential structures or is damaged, deformed or decayed to such an extent that normal development is prevented (see normal seedling). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Abortive
- Abortive. Imperfectly formed of rudimentary. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Abscission
- Abscission. Separation of leaves and other plant parts by the dissolution of the cell wall of a layer of cells. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Abscission layer
- Abscission layer. A layer of cells that forms when a seed becomes separated from its parent plant during development. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Accessory fruit
- Accessory fruit. A fruit, or collection of fruits, whose fleshy parts are derived mostly from tissues other than the ovary. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Accessory structures
- Accessory structures. In seed testing: structures other than the seed and fruit. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Achene


a Calendula officinalis. b Helianthus annuus. c Amberboa moschata. d Tagetes sp. e Zinnia elegans. f Ranunculus sardous. g Adonis aestivalis.
- Achene, achenium. A dry, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit, formed from one free carpel (e.g. Ranunculaceae, Geum) with the seed coat distinct from the fruit coat; occasionally consisting of more than one carpel (Asteraceae). 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Achene, achenium. A dry, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit, formed strictly from one free carpel, and with the testa distinct from the fruit wall, e.g. Ranunculaceae, Geum, occasionally consisting of more that one carpel, e.g. Asteraceae. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Achene. A dry, one-chambered, one-seeded indehiscent fruit with the seed attached to the fruit wall at a single point. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Achene. A one-celled, dry indehiscent fruit in which the testa and pericarp are not firmly attached. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Acotyledonous
- Acotyledonous. An underdeveloped embryo lacking cotyledon(s).SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Acropetal
- Acropetal. Applied to structures that are produced in succession toward the apex. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Acuminate
- Acuminate. Gradually tapering to a sharp point. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111.
-
Acute
- Acute. Sharp at the end but not gradually tapering. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Adaxial
- Adaxial. The side of a lateral organ next to the axis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Adnate
- Adnate. Adhering closely or united. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Adventitious
- Adventitious. Arising out of the ordinary place, as applied to buds or roots. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Adventitious root
- Adventitious root. A root arising from any structure other than a root. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Aeration
- Aeration. In seed testing, to expose to air; cause air to circulate through. Baalbaki, R.Z. Germination & Dormancy. TWS Website. 2020
-
Aggregate
- Aggregate. Collected together in a mass or cluster. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Aggregate fruit
- Aggregate fruit. A fruit derived from a single flower gynoecium comprised of separate carpels. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Albino
- Albino. A seedling in which all tissues are white due to the absence of pigments. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Albino. A seedling that is ‘white’ due to lack of chlorophyll pigments. Baalbaki, R.Z. Germination & Dormancy. TWS Website. 2020
-
Albuminous
- Albuminous. A mature seed containing endosperm (some authors also include perisperm). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Aleurone
- Aleurone. The outer layer of the cells of the endosperm of a caryopsis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Aleurone layer
- Aleurone layer. Outermost layer of endosperm in cereals and many other taxa that contains protein bodies and enzymes concerned with endosperm digestion. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Alternate
- Alternate. The occurrence of buds, leaves, etc., one after another singly at opposite sides of the nodes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Androecium
- Androecium. The stamens considered collectively. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Angiosperm
- Angiosperm. A plant whose seeds are borne within a mature ovary (fruit). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Annual
- Annual. A plant that completes its life cycle and dies in one year. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Anterior
- Anterior. Placed in the front; away from the axis of an inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Anther
- Anther. The pollen-producing part of the stamen, borne at the top of the filament or stalk. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing, (ISTA)
- Anther. Pollen-bearing part of stamen. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Anthesis
- Anthesis. The time during which the flower is open and the anthers are extended from the glumes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Apetalous
- Apetalous. Without petals. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111.
-
Apex
- Apex. The tip, point, or angular summit of a structure. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Apical
- Apical. Belonging to or being at the tip. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Appendage
- Appendage. A subordinate part of a structure. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Appressed
- Appressed. Lying close to an organ. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Archegonium
- Archegonium [archegonia, pl.]. In gymnosperms, a multicellular structure containing a single egg. Also found in bryophytes and lower vascular plants. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Areole
- Areole. The area of seed surface surrounded by the pleurogram. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Aril
-
- Aril, arillus [pl. arilli] a fleshy, of ten coloured covering or appendage of some seeds; an outgrowth of the funicle or base of the ovule (caruncle, strophiole). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Aril. A fleshy outgrowth of the ovule or funiculus. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual. 2018.
-
-
Arista
- Awn, arista. Slender, straight or bent bristle. In grasses: usually a continuation of the mid-nerve of lemmas or glumes. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
-
Aristate
- Aristate. Surface covered with aristae. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Aristate. Tipped with an awn or bristle. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Articulate
- Articulate. Jointed; joined by a line of demarcation between two parts which at maturity separate by a clean-cut scar. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Articulation
- Articulation. The point of union of two articulate organs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Ascending
- Ascending. Sloping upward. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Asexual
- Asexual. Reproduction without involving gametes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Asymmetric
- Asymmetric. Lacking symmetry or correspondence in size and relative position of parts on opposite sides of a dividing line. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Auricle
- Auricle. Applied to ear-like or finger-like lobes at the base of the leaf blades and at the summit of the sheath, as in Hordeae. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Autogamy
- Autogamy. Self-fertilization, as of a flower by its own pollen. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Awn

Seeds with awns. Left to right: Dacty lis glomerata, Festuca rubra, Agropy ron cristatum, Arrhenatherum elatius, Lolium multiflorum, Oryza sativa, Hordeum vulgare.
- Awn, arista. Slender, straight or bent bristle. In grasses: usually a continuation of the mid-nerve of lemmas or glumes. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Awn. The slender bristle extending from the tip ro back of the lemma or the glume of a grass spikelet. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Axil
- Axil. The angle between the leaf or branch and the axis from which it arises. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Axillary
- Axillary. Borne in the axil. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Axis
- Axis. The central line of any organ or the support of a group of organs; the main stem of an inflorescence, especially of a panicle. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
B
-
Barb
- Barb. A hair or bristle ending in a hook. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Basal
- Basal. At the base of bottom. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Basipetal
- Basipetal. Applied to structures that are produced in succession toward the base. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Beak
- Beak [-ed]. A long, pointed prolongation of a fruit. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Beak. A long, pointed prolongation of a fruit (e.g. Anemone, Geranium, Geum). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Beak. A point or projection, as on the glume of a wheat spikelet. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bearded
- Bearded. Bearing long stiff hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Berry
- Berry. A many seeded fleshy indehiscent fruit. The pericarp usually forms a tough outer skin and the mesocarp becomes massive and fleshy. The epicarp and mesocarp may be highly coloured to attract the animals that act as agents of dispersal. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
-
Biennial
- Biennial. A plant that completes its life cycle in its second year of life and then dies. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111.
-
Bifid
- Bifid. Two-cleft or two lobed; applied principally to the summit of lemmas. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bisection
Cut across into two parts. -
Blade
- Blade. The expanded portion of a leaf, usually above the sheath of petiole. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Boerner divider
- Boerner divider. This divider consists of a hopper, a cone, and a series of baffles which direct the seed into two spouts. The baffles are arranged in a circle at the top and form equal width alternate channels and spaces. The channels lead to one spout, the spaces to the other. The width and number of channels and spaces are important. Five channels and spaces should be regarded as a minimum. The more channels the better but the minimum width of the channels must be at least two times the largest diameter of the seed or any possible contaminants being mixed. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Boll
- Boll. The subspherical or ovoid fruit (a dehiscent capsule) of flax or cotton. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Boot
- Boot. The uppermost leaf sheath that serves as a protective covering for the grass inflorescence before it is exserted. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bract
- Bract. A reduced leaf or scale-like structure subtending a flower or a grass spikelet in its axil. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing, (ISTA)
- Bract. In angiosperms: A small or rudimentary leaf or leaf-like structure near the base of a flower or inflorescence. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Bract. A modified leaf associated with a flower or inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bracteole
- Bracteole. A small bract subtending a flower or fruit. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Branch
- Branch. A lateral stem. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bristle
- Bristle. A stiff hair; sometimes applied to the upper part of an awn, when the latter is bent. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Bristle. A stiff hair, the upped part of an bent awn. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Bristle. A short stiff hair. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bud
- Bud. An unexpanded flower or a rudimentary leaf, stem, or branch. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bulb
- Bulb. A short, shoot with modified, thickened leaves, developed as food-storage organs. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Bulb. A short, globose, underground stem bearing many fleshy food-storing scale leaves. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Bulbil
- Bulbil. A small bulb, usually axillary or appearing instead of flowers as in Poa bulbosa, also a bulblet. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
-
Bulblet
- Bulblet. A small bulb; an aerial bulblike structure, usually borne in the axil of a leaf or bract. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Bulk examination working sample
- Bulk examination working sample. The sub-sample taken from the submitted sample on which a bulk examination is performed. Refer to sections 2.3 b and 5.3. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Burr
- Burr. A fruit enclosed in a rough or prickly pericarp, persistent calyx, or involucre with hooks or prickles. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
C
-
Callus
- Callus. The indurate downward extension of the lemma in some grasses. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Calyx
- Calyx [pl. calyces]. The outer floral envelope composed of the sepals. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Calyx [pl. calyces]. The outer floral envelope of dicotyledons, composed of the sepals. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Calyx. The outer cycle of the perianth; the sepals considered collectively. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Capillary
- Capillary. Very slender or hair-like structure. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Capillary bristles
- Capillary bristles. A type of pappus with very slender bristles. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Capitate
- Capitate. Arranged in a head or dense cluster. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Capitulum
- Capitulum. A dense inflorescence of usually sessile flowers. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Capitulum [pl. capitula]. A compact inforescence with a disc of sessile flowers, e.g. Asteraceae (flower head). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Capitulum. A small head inflorescence. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Capsule
- Capsule. A dry, dehiscent fruit derived from two or more-many seeded fused carpels. Capsular fruits are classified by the nature of dehiscence and the number of carpels in each fruit. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Capsule. A dry dehiscent fruit composed of more than one carpel. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cardinate
- Cardinate. Having a keel. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Carpel
- Carpel. The female reproductive organ of flowering plants. It consists of an ovary, containing one or more ovules (which became seeds after fertilization), and a stigma, a surface receptive for pollen grains. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Carpel. A simple pistil or an element of a compound pistil. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Carpophore
- Carpophore. A slender extension of the receptacle between the two carpels of the fruits in some species of the Apiaceae or carrot family. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Cartilaginous
- Cartilaginous. Hard and tough but elastic. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Caruncle
-
Caryopsis
- Caryopsis. In grasses: A dry, one-seeded, indehiscent fruit with the pericarp fused to the seed coat (testa). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Caryopsis. Naked grass-fruit in which the testa is united with the pericarp. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Caryopsis. A naked grass fruit in which the testa is fused with the pericarp; also a grain. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Caryopsis. The fruit of a grass, which is dry, one-seeded, indehiscent, with the testa and the pericarp completely united. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Centrifugal divider
- Centrifugal divider. Gamet type, the divider makes use of centrifugal force to mix and scatter seeds over the dividing surface. The seed flows downward through a hopper onto a shallow rubber cup or spinner. Upon rotation of the spinner by an electric motor the seeds are thrown out by centrifugal force and fall downward. The circle or area where the seeds fall is equally divided into two parts by a stationary baffle so that approximately half the seeds fall in one spout and half in the other spout. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Chaffy seed
- Chaffy seed. Seed units that adhere to other seed units or other surfaces because of their structure or texture, making it difficult to sample a seed lot or mixture and divide a representative working sample. This definition is not applicable to coated, pelleted, encrusted, or hulled seeds that are normally classified as chaffy whether as a single kind under consideration or as components of seed mixtures. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Chalaza
- Chalaza. The region of the ovule opposite the micropyle where the nucellous and integuments fuse with the funiculus. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Chalazosperm
- Chalazosperm. A nutritive tissue within seeds derived from the chalaza. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Chalcid
- Chalcid. Any of various tiny wasps of the superfamily Chalidoidea, some of whose larvae feed inside seed. Examples include, Bruchophagus found in seeds of various Fabaceae and Systole in seeds of various Apiaceae. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Chartaceous
- Cartaceous. Having the texture of writing paper. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Ciliate
- Ciliate. Fringed with hairs on the margin. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Clavate
- Clavate. Club-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cleistogamous
- Cleistogamous. Applied to flowers which are fertilized without opening. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Clone
- Clone. A group of organisms composed of individuals propagated vegetatively from a single original individual. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cluster
- Cluster. A densely crowded inflorescence or, in Beta, part of an inflorescence. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
-
Coleoptile
- Coleoptile. The coleoptile is only present in species of the Poaceae. It is a leaf-like, cylindrical sheath enclosing the terminal bud of the embryo and the developing leaves of the young seedling. The coleoptile provides protection for the leaves as they push up through the soil. After emergence from the soil, growth of the leaves ordinarily causes the coleoptile to split downward from the tip. The coleoptile does not persist beyond the seedling stage. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Coleoptile. The sheath covering the first leaf of a grass seedling. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Coleorhiza
- Coleorhiza. A sheath covering the tip of the first root from a seed. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Collar
- Collar. The area on the outer side of a grass leaf at the junction of sheath and blade. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Columella
- Columella. The axis of a capsule. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Compound leaf
- Compound leaf. A leaf with its blade subdivided into several parts. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Compressed
- Compressed. Flattened laterally. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Conducting tissues
- Conducting tissues. Tissues that transport water and dissolved minerals from the root to the other plant structures, and foods from where they are manufactured (e.g., leaves) to where they are needed for growth or storage. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Contracted
- Contracted. Inflorescences that are narrow with short branches. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Convex
- Convex. Rounded or arching. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Convolute
- Convolute. Rolled longitudinally. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cordate
- Cordate. Heart-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Coriaceous
- Coriaceous. Leathery in texture. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Corm
- Corm. The hard swollen base of a stem which serves for food storage. It involves stem tissue rather than fleshy storage leaves typical of bulbs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111.
-
Corneous
- Corneous. Horny in texture. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Corolla
- Corolla. The inter-cycle of the perianth; the petals considered collectively. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cotyledon
- Cotyledon. The first leaf or pair of leaves of an embryo and seedling, often a food-storage organ. The cotyledons may remain in the seed (hypogeal germination) or emerge to become the first photosynthetic organs (epigeal germination). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Cotyledons. The cotyledons are the storage structures of the embryo. They may be only a small portion of the seed in species with endosperm, perisperm or female gametophyte storage tissue, or they may occupy a large portion of the embryo when they are the primary storage tissue (e.g. Phaseolus vulgaris). In epigeal species, the cotyledons may grow quite large and become the first photosynthetic structures of the young plant. In hypogeal species the primary function of the cotyledons is to provide nutrients to the growing seedling until it can produce its own nutrients. In most species the cotyledons shrivel and drop off as their reserves are depleted. In a few species (e.g. Cucurbita pepo, pumpkin) the cotyledons may persist well beyond the seedling stage of growth. In the monocotyledons the cotyledon absorbs nutrients from the endosperm and transfers them to the growing seedling. In the Poaceae the cotyledon is called the scutellum. It is in close proximity to the endosperm and is laterally attached to the embryo axis. In Allium (Liliaceae) the cotyledon tip remains embedded in the endosperm to absorb nutrients but the cotyledon also emerges from the soil (i.e. germination is epigeal) and becomes photosynthetic. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Cotyledon. The first leaves of the embryo that serve for food digestion and food storage. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cremocarp
- Cremocarp. A type of schizocarp derived from two fused carpels that divides into two one-seeded units at maturity. It is typical of the Apiaceae. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
-
Cross-pollinated
- Cross-pollinated. Pollinated by pollen from another plant. Cross-pollination is usually accomplished by insects or by the wind. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Crosswise
As in diagonally. In a line or direction running from corner to corner. -
Crown
- Crown. The persistent base of tufted herbaceous perennials from which new shoots and new roots arise. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Culm
- Culm. The jointed stems of grasses. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cuticle
- Cuticle. A thin waxy covering over the outer walls of epidermal cells. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cylindrical
- Cylindrical. Having the form of a cylinder. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Cypsela
- Cypsela. A fruit similar to an achene except that it develops from an inferior ovary, and thus also includes non-carpellary tissue. It is typical of the Asteraceae, in which the fruit is surrounded by hairs derived from the calyx. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
D
-
Dead seeds
- Dead seeds. Seeds which at the end of the test period are neither hard nor dormant nor have produced any part of a seedling. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Decay
- Decay. Break-down of organic tissue, usually associated with the presence of microorganisms. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Deciduous
- Deciduous. Not persistent; falling away at maturity or in season. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Decumbent
- Decumbent. Curved upward from a horizontal or inclined position with tip ascending. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dehiscence
- Dehiscence. Opening at maturity by means of pores, valves, slits, etc., as in the case of a capsule or an anther. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dehiscent
- Dehiscent. A fruit in which the fruit wall splits opens at maturity to release the seed. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Dehiscent. Opening spontaneously at maturity. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Dehiscent fruit
- Dehiscent fruit. A dry fruit, that experiences desiccation. Seeds within dehiscent fruits will lose moisture content during the later stages of seed development. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
- Dehiscent fruit. A fruit that opens at maturity allowing seeds to be released from the fruit. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Deltoid
- Deltoid. Triangular. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
-
Dense
- Dense. Parts massed or crowded together. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dentate
- Dentate. Having a toothed margin, as a leaf. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Diadelphous
- Diadelphous. Filaments of the stamens united into two sets. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Diaphanoscope
- Diaphaniscope. A device with a strong beam of light directed up through a piece of glass over which the internal structure of a seed unit can be examined. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Dichogamy
- Dichogamy. Maturation of stamens and pistils at different times. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dichotomous
- Dichotomous. Division of a class into two subclasses, especially two opposed by contraction, as white and not white. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dichotomous key
- Dichotomous key. A series of paired statements comparing features and used as a diagnostic tool. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Dicotyledon
- Dicotyledon. Plants with two cotyledons or seed leaves. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Differentiation
- Differentiation. The process by which different cell types are formed. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Diffuse
- Diffuse. Spread widely or loosely. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Digitate
- Digitate. Diverging like the fingers spread. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dimorphic
- Dimorphic. An object having two forms. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Dioecious
- Dioecious. Bearing staminate flowers on one plant and pistillate on another. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Disarticulate
- Disarticulate. Separate at a joint at maturity (see articulate). Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Diseased
- Diseased. Showing symptoms of the presence and activity of pathological or detrimental micro-organisms. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Distal
That farthest from the stem-root junction or the plant and nearest to the tip of the shoot or root. -
Distichous
- Distichous. Arranged in two vertical rows. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Divergent
- Divergent. Deviating from a common axis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dormancy
- Dormancy. Delayed germination or growth; a condition of inactivity. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Dormant seeds
- Dormant seeds. Viable seeds, other than hard seeds, which fail to germinate when provided the specified germination conditions for the kind of seed in question. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Dorsal
- Dorsal. The side facing away from the axis; the upper part. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010.
- Dorsal. Relating to the back of a structure of organ. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Dorsal
In general, "dursal" refers to "the rear or back or upper surface." -
Dorsiventral
- Dorsiventral. Extending from the dorsal to the ventral side, as the dorsiventral axis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Drupe
- Drupe. Indehiscent, one-seeded fruit with stony endocarp and fleshy outer layers. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Drupe. A fleshy indehiscent fruit in which the seed or seeds are surrounded by a hardened en-docarp, as in Prunus avium. The endocarp may replace the testa in its protective role, and may also play part in the dormancy mechanism. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Drupe. An indehiscent fruit with a fleshy outer layer and a stony inner layer surrounding the seed. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Drupelet
- Drupelet. A small drupe, as one section of a blackberry. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Dry fruits
- Dry fruits. Fruits in which the middle layer of the pericarp, the mesocarp, does not develop into a fleshy covering. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
E
-
Ellipsoidal
- Ellipsoidal. A solid body elliptical in section. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Elliptical
- Elliptical. Shaped like an ellipse. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Elongate
- Elongate. To stretch out or lengthen. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Emarginate
- Emarginate. Having the margin notched. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Embryo
- Embryo. The young plant enclosed in a seed. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Embryo. Rudimentary plant enclosed in a seed, usually consisting of a more or less differentiated axis and attached cotyledon(s). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- The embryo. The product of one of the fusions of the angiosperm fertilization process is the embryo (the other being the endosperm). In gymnosperms the embryo is the only product of the fertilization process. Depending on the species, the embryo develops to varying degrees within the seed, becoming a "miniature plant" by the end of the growing season. In Phaseolus vulgaris, for example, the embryo is fully developed and the radicle, hypocotyl and epicotyl with primary leaves can easily be observed. The development of the embryo in other species may be much less, with some essential structures being observed only after considerable growth of the seedling. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Embryo. A young plant before the beginning if its rapid growth. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Embryo excision test
- Embryo excision test. Excising the embryo from the seed coat and associated structures that often impose dormancy to permit germination. Often used as a viability test for dormant tree and shrub seeds.SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Embryo sac
- Embryo sac. A large thin-walled cell within the ovule in which the embryo develops after fertilization. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Endocarp
- Endocarp. The inner layer of the pericarp. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Endocarp. The innermost layer(s) of the pericarp (fruit wall). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Endogenous
- Endogenous. Originating from deep tissue or from within the seed, as in production of gibberillins by the embryo. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Endosperm
- Endosperm. Nutritive tissue originating from fertilization and retained at maturity in some seeds as a storage tissue for food reserves. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Endosperm.The nutritive tissue developed as a result of fertilization associated with the embryo in seeds. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
- Endosperm. Endosperm is one of the products of double fertilization, and in some species, particularly those of the Poaceae, it develops as the storage tissue. In this event, little or no nucellus tissue remains, and the extent of cotyledon development varies. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Entire
- Entire. Without divisions, lobes, or teeth; usually refers to margins of leaves, petals, and sepals. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Epiblast
- Epiblast. A scale-like structure opposite the scutellum in the embryo of some grasses. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Epicarp
- Epicarp. The outer layer of the pericarp. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Epicotyl
- Epicotyl. In Dicotyledons and gymnosperms, the epicotyl includes all seedling structures above the cotyledons. In species with epigeal germination (e.g. Phaseolus vulgaris), the epicotyl, cotyledons and part of the hypocotyl emerge from the soil. In species with hypogeal germination (e.g. Pisum sativum), only the epicotyl emerges, carrying the first foliage leaves above the soil surface. In these species, the epicotyl also bears one or more scale leaves. Dormant meristematic buds in the axils of these scale leaves become active if there is damage to the terminal bud. The conducting tissue of the epicotyl transfers water and nutrients from the hypocotyl and cotyledons to the leaves and terminal bud above. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Epicotyl. The stem of the embryo or young seedling above the cotyledons. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Epidermis
- Epidermis. The surface layer of cells of leaves and other soft plant parts. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Epigeal
- Epigeal. Cotyledons borne above the ground after germination (see hypogeal). Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Epigeal germination
- Epigeal germination. A type of germination in which cotyledons are carried above soil level by the elongating hypocotyl (see hypogeal germination). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Equilibrium relative humidity
- Equilibrium relative humidity. The relative humidity of the atmosphere in an enclosed environment that surrounds a seed (or any moisture absorbent object), at which the seed will neither lose nor gain moisture. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Essential structure
- Essential structure. Structure which is critical for continued development of the seedling into a plant. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual. 2018
- Essential structure. Any seedling structure that must be considered when classifying a seedling as either normal or abnormal. In general, an essential structure is one that is critical for successful establishment and development of a seedling into a plant. Structure which is critical for continued development of the seedling into a plant. Baalbaki, R.Z. Germination & Dormancy. TWS Website. 2020
-
Etiolate
- Etiolate. Characterization of plants grown in the absence of light: involves abnormal stem elongation and absence of chlorophyll. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Etiolated
- Etiolated. Lengthened or deprived of color by absence of light. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Exalbuminous
- Exambuminous. A mature seed without endosperm. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Excurrent
- Excurrent. Running out as a nerve of a leaf running out beyond the margin. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Exserted
- Exserted. Protruding past surrounding organs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Extravaginal
- Extravaginal. Referring to branches in grasses which force their way out through the base of the leaf sheath. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
F
-
Falcate
- Falcate. Curved sidewise and flat, shaped like a scythe. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
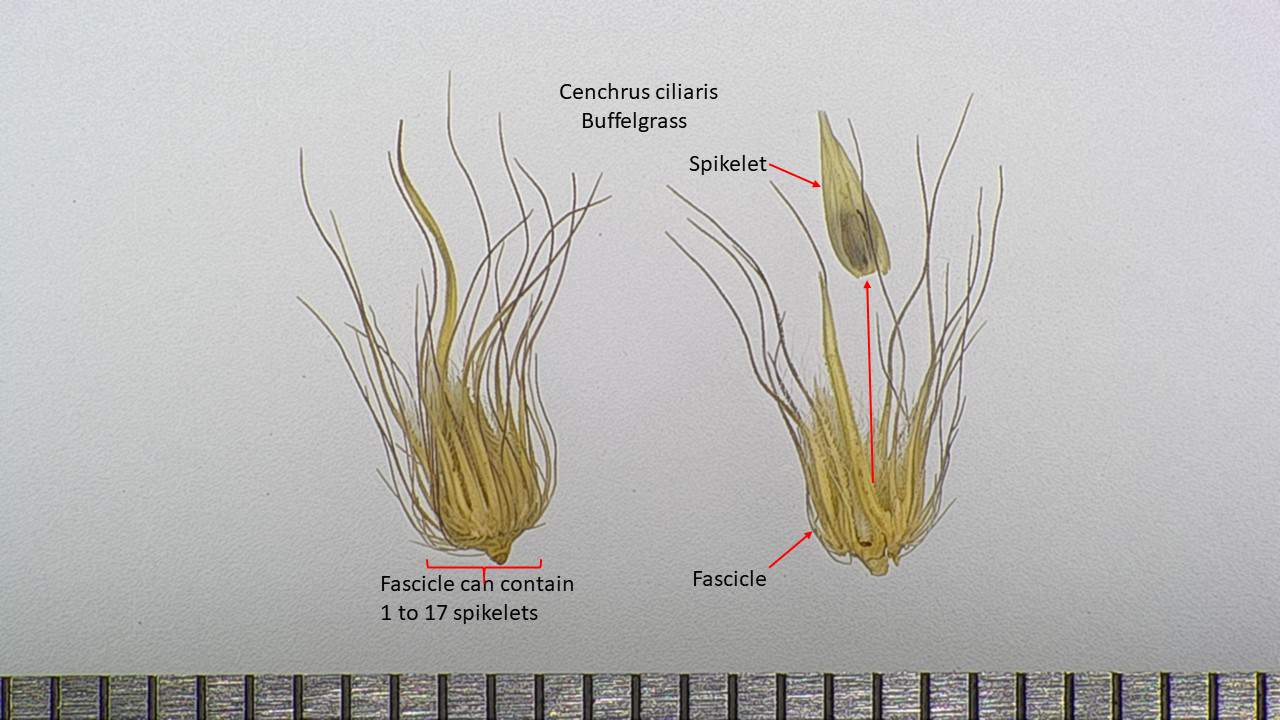
Fascicle
- Fascicle. A tuft of branches arising from about the same place. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Fascicle. A little cluster. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
- Fascicle. In grasses: A group of spikelets subtended by bristles. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Image
-
Female gametophyte
- Female gametophyte. In gymnosperms the nutritive tissue is the mature female gametophyte, sometimes also referred to as the primary endosperm because it is already present before fertilization. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Fertile
- Fertile. With functional sex organs; (for grass florets: having a caryopsis). 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Fertile. With functional sex organs. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Fertile. Capable of producing fruit; having pistils. A fertile floret may be pistillate or perfect. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Fertile floret
- Fertile floret. A floret that encloses a caryopsis. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Fertilization
- Fertilization. A sexual process in which two dissimilar gametes fuse. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Fibrous
- Fibrous. Fiber-like, usually referring to root system of many small thread-like roots. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Filament
- Filament. The slender stalk that bears the anther. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Filament. Thread-like stalk of a stamen. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Filiform
- Filiform. Having a thread-like shape. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Flabellate
- Flabellate. Fan-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Fleshy fruits
- Fleshy fruits. Fruits that retain moisture. Seeds within fleshy fruits remain at a high moisture content throughout seed development. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Flexuous
- Flexuous. Bent alternately in opposite directions. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Flora
- Flora. A list of plants growing in a defined geographic region. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Floret
- Floret. General: An individual flower within a cluster. In grasses: A flower usually enclosed by two bracts (lemma and palea). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Floret. A flower within an inflorescence or in a grass spikelet. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
- Floret. The lemma and palea with enclosed pistil and stamens, or, in Poaceae, the mature caryopsis; for the purpose of the Rules, the term floret refers to the fertile floret, with or without additional sterile lemmas. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Floret. The lemma and palea with enclosed pistil and stamens or the mature caryopsis in Poaceae; for the purpose of the Rules, the term floret refers to the fertile floret with or without additional sterile lemmas. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Floret. In grasses, a flower consisting of lemma and palea which enclose the flowering parts -- stamens, pistil and lodicules. May be perfect, staminate, pistillate, neuter, sterile, and so on. A small flower in other plant families. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Flower head
- Flower head. A dense cluster of sessile flowers on a very short axis (capitulum). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Follicle
- Follicle. A dry, dehiscent, many-seeded fruit derived from one carpel, which on ripening splits down one side only (usually the ventral suture) to expose the seeds, as in Delphinium. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Follicle. A many-seeded dry fruit, derived from a single carpel, and splitting longitudinally down one side. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Fresh and dormant
- Fresh and dormant. Newly harvested seed. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Fruit
- Fruit. The structure that develops from the pericarp as the enclosed seed or seeds mature. Fruits may have the following attributes: Succulent or dry, depending on whether or not the middle layer of the pericarp (mesocarp) develops into a fleshy covering; Dehiscent or indehiscent, according to whether or not the fruit wall splits open to release the seed; True or simple fruits, which develop from the gynoecium of a single flower, and multiple fruits, which develop from a complete inflorescence; Monocarpellary or polycarpellary, depending on whether they developed from a single ovary or from a number of fused ovaries. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Fruit. In angiosperms, a mature ripened ovary, usually containing seeds. Some authors include extracarpellary parts adhering to the ovary at maturity. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
- Fruit. The ripened ovary of a seed plant and associated parts. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Fruiting bract
- Fruiting bract. A small or rudimentary leaf or leaf-like structure near the base of a fruit that may or may not enclose the fruit. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Funicular remnant
- Funicular remnant. A piece of funiculus remaining attached to the seed. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Funiculus
-
Fusiform
- Fusiform. Tapering at each end. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
G
-
Gamete
- Gamete. A matured sex cell capable of uniting with another gamete to form a new individual. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Geniculate
- Geniculate. Bent abruptly like a knee. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Genus
- Genus. A group of closely related species. The genus name is the first word of a binomial scientific name and is capitalized. The plural form of the word is genera. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Geotropism
- Geotropism. Plant growth response to gravity. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Germination
- Germination. Germination of a seed in an ISTA test is the emergence and development of the seedling to a stage where the aspect of its essential structures indicates whether or not it is able to develop further into a satisfactory plant under favourable conditions in the field. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing, (ISTA)
- Germination (seed testing definition).The emergence and development from the seed embryo of those essential structures which, for the kind of seed in question, are indicative of its ability to produce a normal plant under favorable conditions. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Germination (physiological definition). A process involving water uptake, metabolic changes and cell elongation resulting in radicle emergence from the seed. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Germination working sample
- Germination working sample. The sub-sample taken either from the pure seed portion of the purity analysis or directly from the submitted sample on which the germination test is performed. Refer to sections 2.3 c and 6.1. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Gibberellic acid
- Gibberellic acid. A growth hormone, one of over 50 gibberellins. First discovered in the fungus Gibberella fujikuroi. Found in highest concentrations in immature seeds. Can be used to substitute for dormancy-breaking cold and light requirements in many species. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Gibberellins
- Gibberellins. Growth hormones that stimulate cell division and cell elongation. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Glabrous
- Glabrous. Smooth, without hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Glandular
- Glandular. Bears organs for secreting a substance or substances. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Glaucous
- Gloucous. Covered with a powdery wax coating such as found on a Concord grape. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Globose
- Globose. Shape is spherical or nearly so. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Glume
- Glume. In grasses: A bract—often paired—at the base of a spikelet. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Glume. One of the two usually sterile bracts at the base of a grass spikelet. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Glumes. The pair of empty bracts at the base of a spikelet. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Grain
- Grain. The seed-like fruit of any cereal. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Gravimetric
- Gravimetric. Determined by weighing. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Gregarious
- Gregarious. Growing in groups or colonies. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Growth hormone
- Growth hormone. A chemical compound generally produced in one part of an organism and transported to another part of the organism where it controls and affects growth and development. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Gynoecium
- Gynoecium. The female reproductive part of a flower, composed of one or more pistils. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Gynoecium. The carpels taken collectively. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
H
-
Hair
-
Hairy
- Hairy. Bearing hairs. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Hard seeds
- Hard seeds. Seeds which remain hard at the end of the prescribed test period because they have not absorbed water due to an impermeable seed coat. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Head
- Head. A type of inflorescence with sessile or nearly sessile flowers on a very short axis or receptacle, as in a sunflower. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Herbaceous
- Herbaceous. Describing plants which do not develop much woody tissue but remain soft and succulent. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Hesperidium
- Hesperidium. A type of berry with a leathery epicarp, such as a citrus fruit. Fluid filled trichomes fill the locule of each carpel to form the characteristic segments. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Heterogeneous
- Heterogeneous. Having unlike qualities. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Heterogeneous seed sample of lot
- Heterogeneous seed sample or lot. A sample or lot which is not uniform throughout in one or more characteristics. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Hilum
- Hilum. Scar on a seed coat marking the place of attachment of the seed stalk to the seed. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Hirsute
- Hirsute. Pubescent with rather straight stiff hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Hispid
- Hispid. Pubescent with stiff or rigid hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Histeresis
- Hysteresis. The effect where at a given relative humidity seeds will have a different moisture content dependent on whether they are absorbing (gaining) or desorbing (losing) moisture. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Histo-differentiation
- Histo-differentiation. The differentiation of cells in an embryo. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Homogeneous
- Homogeneous. A sample or seed lot which is uniform throughout. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Hulled seed
- Hulled seed. Seed units ordinarily with various structures, including but not limited to wings, hairs, spines, awns, sterile florets, calyces, etc., attached to or surrounding the seed (or caryopsis) that have these structures partially or completely removed during seed conditioning to improve seed flow and plantability. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Hyaline
- Hyaline. Thin and translucent or transparent. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Hydration
- Hydration. The act of becoming chemically combined with water. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Hydrolyzed
- Hydrolyzed. Chemically decomposed by taking up the elements of water. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Hygroscopic
- Hygroscopic. The phenomenon where seeds will take up or lose water until they have reached the same relative humidity as that of their environment. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species, TWS Website, 2020.
-
Hypanthium
- Hypanthium [pl. hypanthia]. A ring-like, cup-like or tubular structure which surrounds the ovary and on which sepals, petals and stamens are borne. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Hypanthium. A cup-shaped structure surrounding the ovary, derived either from the fusion of floral parts or an extension of the receptacle to which the floral parts are attached. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Hypocotyl
- Hypocotyl. The portion of the seedling axis between the root and the cotyledons is the hypocotyl. The hypocotyl is a transition structure for the transport of water and dissolved salts from the roots to the epicotyl. When a seed with epigeal germination (see section 2.5 for definitions of epigeal and hypogeal germination) is planted in moist soil, the hypocotyl elongates carrying the cotyledons above the soil surface. In monocotyledons the hypocotyl is usually not discernible as a separate structure. The mesocotyl is the part of the seedling axis between the scutellum and the base of the coleoptile. In some species (e.g. Zea mays) the elongation of the mesocotyl may be considerable. In others (e.g. Triticum aestivum) the elongation may be imperceptible. Elongation of the mesocotyl is suppressed by light after the coleoptile emerges from the soil. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Hypocotyl. That portion of the embryo stem below the cotyledons. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Hypogeal
- Hypogeal. The cotyledons borne below the ground after germination (see epigeal). Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Hypogynous
- Hypogynous. A flower with sepals, petals, and stamens attached to the receptacle below the ovary (superior ovary). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
I
-
Imbibition
- Imbibition. The uptake of water by the seed from the germination substrate. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Imbricate
- Imbricate. Overlapping like shingles on a roof. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Impaired
- Impaired. Unable to function normally, in reference to damaged seedling structures. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Incise
Cut deeply. -
Indehiscent
- Indehiscent. Not opening; fruits which do not open at maturity. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Indehiscent. Fruits in which the fruit wall does not split open at maturity to release the seed (see dehiscent). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Indehiscent fruit. A fruit that does not open at maturity. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Indehiscent. Fruits remaining closed at maturity. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Indigenous
- Indigenous. Native to the region of growth. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Indurate
- Indurate. Hardened. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Inert matter
- Inert matter. Inert matter shall include seeds and seed-like structures from both crop and weed plants and other materials not described in section 3.2 and Table 3A or can be described as follows: seeds and seed-like structure from crop and weed plants and other non-seed matter. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Infection
- Infection. Entrance and spread of disease organisms in living material (e.g., seedling structures) often causing disease symptoms and decay. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Inferior ovary
- Inferior ovary. An ovary completely or partially surrounded by floral parts of embedded in receptacle tissue. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Inflated
- Inflated. Puffed up, bladdery. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Inflexed
- Inflexed. Turned in at the margins. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Inflorescence
- Inflorescence. A flower cluster. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Inflorescence. The portion of the plant adapted for flowering and fruiting. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Inhibitor
- Inhibitor. A chemical substance that retards or prevents germination. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Inner membrane
- Inner membrane. A complex tissue derived from seed testa and endosperm found in seed in the family Asteraceae. The site of impermeability to water and gases in this group. This membrane is sensitive to temperature when hydrated, and is the site of phytochrome responses to light. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
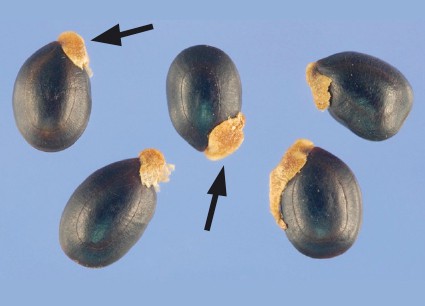
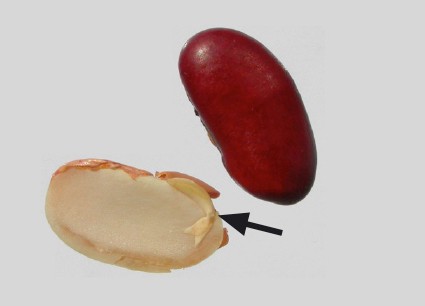
Integument

Integument. Winged seed of Pinus nigra (with attached integument) and fragment of integument, i.e. inert mat- ter (arrow).
- Integument. The envelope of an ovule which becomes the seed coat or testa (generally two integuments present). In coniferous seeds integument also refers to the tissue attaching the wing to the seed. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Integument. The envelope of an ovule, which becomes the testa. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Integuments. Outermost coverings of an ovule. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Internode
- Internode. The part of a stem between two nodes. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Internode. Portion of a culm or stem between two nodes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Interrupted
- Interrupted. Continuity broken. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Intravaginal
- Intravaginal. A type of branching in grasses with the branches growing out between the leaf sheath and the culm (stem). Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Involucei
- Involucel. A secondary involucre; often around a cluster of flowers. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
-
Involucel
- Involucel. Group of bracts, loose outer calyx (e.g) Scabiosa); a secondary involucre; often around a cluster of flowers. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Involucre
- Involucre. Ring of bracts or bristles surrounding the base of an inflorescence. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Involucre. Ring of bracts or bristles surrounding the base of an inflorescence such as a capitulum (Asteraceae) or umbe (Apiaceae). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Involucre. A whorl of bracts, which may or may not be fused, subtending a flower or group of flowers. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Involucre. A circle of bracts or bristles surrounding a flower or a cluster of flowers. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Involute
- Involute. Rolled inward. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Irregular
- Irregular. One or more of the parts of a series, usually of a flower, are dissimilar. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Isotherm
- Isotherm. The relationship between moisture content and relative humidity. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
J
-
Joint
- Joint. The place or part where two things are joined, as a node. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
K
-
Keeled
- Keeled. Shaped like the keel of a boat with a central ridge. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Kernel
- Kernel. A seed within a stone. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Kernel. A whole grain or caryopsis of a cereal. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Kind (of seed)
- Kind (of seed). One or more related species or subspecies that singly or collectively is usually known by one common name. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
L
-
Lanceolate
- Lanceolate. Several times longer than wide, tapering from base to apex; lance-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Lateral
Attached to the side of an organ. Cut lengthwise. -
Laterally flattened
- Laterally flattened. Compressed from the sides, that is, flattened along the axis to spread the glumes apart. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Lax
- Lax. Loose or open, not crowded. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Leaf
- Leaf. Lateral organ of the stem. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Leaflet
- Leaflet. One of the divisions of a compound leaf blade. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Legume
- Legume. A dry fruit consisting of one carpel, splitting by two longitudinal sutures with a row of seeds on the inner side of the central suture; pod, as in Fabaceae. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Lemma
- Lemma. The outer (lower) bract of a grass floret, sometimes referred to as the flowering glume or the lower or outer palea. Bract enclosing the caryopsis on the outer (dorsal) side. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Lemma. The outer (lower) bract of a grass floret; enclosing the caryopsis on the outer (dorcal) side. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Lemma. The lower of two bracts that subtend a grass flower. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Lemma. The lower of the two bracts enclosing the flower in the spikelet of grasses. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Lens
- Lens. A protuberance, usually located on the side of the hilum opposite the micropyle in some Fabaceae seed. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Lesion
- Lesion. In seedlings of dicotyledons the root-shoot axis is made up of a central stele (or cylinder), surrounded by cortex and epidermis. The conducting tissues are in a concentric ring forming the outer layers of the stele, and serve to transport water and nutrients. In the seedling descriptions, deep open cracks extending into the conducting tissue of the hypocotyl or epicotyl are considered to be abnormalities, for two reasons: (a) interference with movement of water and nutrients through the affected area, and (b) increased susceptibility of the seedling to micro-organism attack. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Ligule
- Ligule. The thin appendage or ring of hairs on the inside of a leaf of grasses at the junction of sheath and blade. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Linear
- Linear. Long and narrow, its sides nearly parallel. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Lobe
- Lobe. A segment of an organ, usually rounded or obtuse. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Locule
- Locule, loculus (pl. loculi). Compartment of the ovary containing the seeds. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Locule, loculus (pl. loculi). A compartment of the ovary containing the ovules, and later, seeds. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Locule. One of the cavities of an ovary. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Lodicule
- Lodicule. The organs at the base of the ovary of a grass flower that swell and open the lemma and palea during anthesis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Lodicules
- Lodicules. Scale-like structures in a grass flower that swell and force ope the surrounding structures to facilitate pollination. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Lomentum
- Lomentum. A dry, dehiscent fruit developed from a single carpel containing one or more seeds. It resembles a pod, but on ripening a false septum divides the pod into one-seeded units of valves that fracture at maturity, as in Onobrychis viciifolia. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Longitudinal
Running lengthwise rather that across.
M
-
Marginal
- Marginal. Near the edge. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Mass maturity
- Mass maturity. The stage of seed development where a seed reaches maximum dry weight. This corresponds with the time at which the seed becomes detached from the parent plant. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Mechanical dividers
- Mechanical dividers. This method is suitable for most kinds of seeds. The apparatus divides a sample into two approximately equal parts. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Membranaceous
- Membranaceous. Thin, soft tissue, more of less translucent. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Mericarp
- Mericarp. A segment from a schizocarpic fruit. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Mericarp. Part of the schizocarp. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Mericarp. One section of a two- to many-sectioned schizocarpic fruit, separating at maturity into indehiscent one-seeded mericarps (e.g. Apiaceae with two mericarps, Malvaceae with several mericarps, Geraniaceae, Tropaeolaceae). A mericarp origi- nates from an entire carpel (see also nutlet). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Mesocarp
- Mesocarp. The middle layer of the pericarp. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Mesocarp. The middle layer of the pericarp (fruit wall) between the endocarp and exocarp. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Mesocotyl
- Mesocotyl. A term applied to the sub-crown internode of a grass seedling. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Micropylar region
- Micropylar region. Area around the micropyle. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Micropyle
- Micropyle. The opening in the integuments of the ovule that permit the entry of the pollen tube to allow fertilization. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Micropyle. Minute opening in the integuments of an ovule through which the pollen tube penetrates to the embryo sac. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Minute
Two definitions: 1. MINute - a small measure of time. 2. minUTE - a small thing. -
Monadelphous
- Monadelphous. Having the filaments united into a single tube around the pistil. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Moniliform
- Moniliform. Jointed or constricted at regular intervals, like a string of beads. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Monocarpellary
- Monocarpellary. Derived from a single ovary. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Monocotyledon
- Monocotyledon. Plant having one cotyledon, as in the grass. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Monoecious
- Monoecious. Bearing stamens and pistils in separate flowers on the same plant. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Morphological dormancy
- Morphological dormancy. Seed dormancy due to immaturity of the embryo. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Morphology
- Morphology. The study of form and structure of an organism. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Morphophysiological dormancy
- Morphophysiological dormancy. Dormancy combining embryo immaturity and physiological dormancy. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Mucilaginous
Resembling mucilage: moist, ropy, slimy and sticky. -
Mucro
- Mucro. Minute awn or excurrent mid-nerve of an organ. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Multiple fruit
- Multiple fruit. A fruit which develops from a complete inflorescence, as opposed to a true or simple fruit, which develops from one flower. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Multiple seed unit
- Multiple seed unit. Spikelet or part of spikelet with more than one floret, with or without glumes. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Multiple unit. Is a seed unit that includes one or more structures as follows: (1) An attached sterile or fertile floret that extends to or beyond the tip of a fertile floret; (2) A fertile floret with basally attached glume, glumes, or basally attached sterile floret of any length; (3) A fertile floret with two or more attached sterile and/or fertile florets of any length. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Multiple unit procedure
- Multiple unit procedure. A purity procedure used to determine the amount of inert material in spikelets and florets that do not disarticulate in certain prescribed grasses by means of a mathematical factor method. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
N
-
Navicular
- Navicular. Boat-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Necrosis
- Necrosis. Dead or deteriorating seedling tissue, that may be caused by injury, disease or physiological breakdown. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Negative geotropism
- Negative geotropism. Negative geotropism is caused by a physiological disorder usually characterized by root structures that grow upward. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Nerve
- Nerve. Vascular veins of the blades, glumes and lemmas. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Nerved
- Nerved. Having pronounced veins. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Neuter
- Neuter. Without stamens or pistils. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Nodding
- Nodding. Inclined from the vertical. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Node
- Node. The point on a stem from which a leaf arises. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Nodule
- Nodule. An enlargement on the roots of legumes within which the nitrogen-fixing bacteria live. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Normal seedling
- Normal seedling. A seedling with all essential structures present and capable of developing into a plant under favorable conditions; certain defects may be present if they are judged to be not so severe as to impede further development of the plant (see abnormal seedling). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Noxious working sample
- Noxious weed seed examination working sample. The sub-sample taken from the submitted sample on which the noxious weed seed examination is performed. Refer to sections 2.3 b and 5.1. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Nucellus
- Nucellus. The ovule tissue within the integuments around the embryo sac. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Nut
- Nut. A dry indehiscent fruit with a hard wall that is usually shed as a one-seeded unit. It forms from more than one carpel, but only one seed develops, the rest aborting. The pericarp is usually lignified and is often partially or completely surrounded by a cupule. True nuts include the acorn (Quercus), hazelnut (Corylus) and beechnut (Fagus). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Nut. A hard, dry, indehiscent fruit, usually single-seeded. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Nutlet
- Nutlet. A small nut. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Nutlet. A small nut, a one seeded portion of a fruit originating from half of a carpel (e.g. Boraginaceae, Lamiaceae and Verbinaceae). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Nutlet. A dry, one-seeded, indehiscent section of a fruit in the Boraginaceae, Lamiaceae and Verbenaceae. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
O
-
Obcordate
- Obcordate. Heart-shaped with broad end at the tip. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Oblanceolate
- Oblanceolate. Lanceolate with broadest part at the apex. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Oblique
- Oblique. Slanting or inclined. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Oblong
- Oblong. Longer than broad with sides nearly parallel. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Obovate
- Obovate. Egg-shaped outline with broadest end above. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Obsolete
- Obsolete. Greatly reduced in size so as to be difficult to see. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Obsolete. Almost absent or vestigial. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Obtuse
- Obtuse. Blunt or rounded. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Open
- Open. Loose; opposite of dense or compact. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Opposite
- Opposite. Bearing two leaves or buds at a node on opposite sides of a stem. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Order
- Order. A category in the classification of plants ranking below class and above family; an order is composed of families. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Orthodox
- Orthodox. Desiccation tolerant. Capable of surviving drying to very low moisture contents. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Other crop seed
- Other crop seed. Seeds of plants grown as crops (other than the kind(s) and cultivar(s) included in the pure seed) shall be considered other crop seeds, unless recognized as weed seeds by laws, regulations, or by general usage; refer to section 4. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Other crop. Species that are usually involved in seed commerce but are not intended to be part of the seed lot being tested. Contamination by these seeds is undesirable in the seed lot but not usually harmful. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 3, 2019
-
Other seeds
- Other seeds. Other seeds shall include seed units of any plant species other than that of pure seed. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing, (ISTA)
-
Ovary
- Ovary. The basal, expanded part of the pistil that contains the ovules. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Ovary. The basal enlarged portion of a pistil within which seeds develop. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Ovate
- Ovate. Egg-shaped, broadest part at base. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Oven test method
- Oven test method. Seed moisture test in which a quantity of seed is weighed prior to and after drying in an oven at a prescribed temperature for a specified time and the loss in weight is calculated as percentage moisture content on a fresh or dry weight basis. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Ovule
- Ovule. The immature seed within the ovary. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Ovule. A structure, consisting of a female gametophyte, nucellus, and integuments, which develops into a seed after fertilization. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Ovulode
- Ovulode. An ovule that did not develop into a mature seed, as in Eucalyptus spp. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
P
-
Paired tests
- Paired test. Test procedures used on seeds having an unknown degree of dormancy. Samples are tested both with and without prechill or other treatments prescribed for breaking dormancy. Refer to section 6.9 n (3) for trees and shrubs. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Palea
- Palea. The upper (inner) bract of a grass floret, sometimes called the inner or upper palea. Bract enclosing the caryopsis on the inner ventral side. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Palea. The upper (inner) bract of a grass floret, the bract enclosing the caryopsis on the inner (ventral) side. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Palea. The uppermost of two bracts subtending a grass flower. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Palea. The upper of the two bracts enclosing the flower in the spikelet of grasses. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Palmate
- Palmate. Having lobes radiating from a common point; refers especially to leaf blades. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Panicle
- Panicle. A compound inflorescence with a main axis which has branches, each of which bears pedicellate spikelets. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Papilla
- Papilla. An epidermal cell forming a conical protuberance like a minute hair. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Papillionaceous
- Papillionaceous. Butterfly-shaped, as the flower of some legumes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Papillose
- Papillose. Covered with, or bearing, papillae. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pappus
- Pappus. A ring of fine, sometimes feathery hairs or scales, crowning an achene. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Pappus. A ring of fine, sometimes feathery hairs or scales, crowning an achene in Asteraceae. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pappus. The teeth, awns, etc., surmounting the achene of the Asteraceae family. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pectinate
- Pectinate. Having teeth-like projections, giving a comb-like appearance. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pedicel
- Pedicel. The stalk of each single flower in an inflorescence. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Pedicel. A small stalk, the stalk of a single flower in an inflorescence. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pedicel. The stalk of a floret in an inflorescence or of a grass spikelet. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Pedicel. The stalk of an individual flower or spikelet of an inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pedicellate
- Pedicellate. Having, or attached by, a pedicel. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Peduncle
- Peduncle. The stalk or stem bearing an inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pendant
- Pendant. Hanging down. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pepo
- Pepo. A type of berry with a hard exterior, derived from either the epicarp or the non-carpellary tissue of the plant. In the Cucurbitaceae, the hard exterior is formed from the receptacle of the flower. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Perennial
- Perennial. Living more than one year. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Perfect flower
- Perfect flower. Having both stamens and pistil. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Perianth
- Perianth. A collective term for the calyx and corolla of a flower. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Perianth. The two floral envelopes (calyx and corolla) or any one of them. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Perianth. The floral envelope, including the calyx and/or corolla, that can remain unwithered and often enlarged around the fruit (e.g. in Kochia). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Perianth. The floral envelope including the calyx and corolla. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pericarp
- Pericarp [fruit coat]. The wall of the mature ovary or fruit. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Pericarp. The ovary wall. the fruit coat enclosing the seed. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pericarp. Fruit wall. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Pericarp. The wall of a ripened ovary; the fruit coat. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Perisperm
- Perisperm. The nucellus may persist as the storage tissue, in which case it is referred to as "perisperm". In Beta vulgaris (beet) the storage tissue is perisperm and there is little or no development of the endosperm following fertilization. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Persistent
- Persistent. Remaining attached after other parts have been shed. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Petal
- Petal. One of the divisions on a corolla; a showy floral leaf of the perianth. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Petiole
- Petiole. The stalk of a leaf. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Physical dormancy
- Physical dormancy. A type of dormancy due to the impermeability of seed (or fruit). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Physiological dormancy
- Physiological dormancy. A physiological inhibiting mechanism of the embryo that prevents radicle emergence. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Pilose
- Pilose. Covered with soft hair. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pinnate leaf
- Pinnate leaf. The leaflets of the leaf blade arranged on each side of the common rachis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pistil
- Pistil. A part (or whole) of the gynoecium, consisting of either a separate, free carpel or two or more fused carpels. A typical pistil comprises an ovary, a style and a stigma. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pistil. The ovule-bearing portion of a flower consisting of a stigma, style and ovary. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pistillate
- Pistillate. Having a pistil. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Placenta
- Placenta. The part of the ovary where the funicles attach. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Plumose
- Plumose. Feathery; as an axis with fine hairs or bristles on both sides. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Plumose. Feathery. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Plumule
Plumule. The apex of the embryo axis; the embryonic shoot above the cotyledons. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010 -
Pod


Pods. a Securigera varia. b Melilotus albus. c Medicago lupulina. d Medicago sativa. e Onobrychis viciifolia. Robinia pods
- Pod. Dehiscent dry fruit, especially of Fabaceae. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Pod. A dry dehiscent fruit, especially in Fabaceae, formed from a single carpel (containing one or more seeds) which on ripening splits along the ventral and dorsal sutures to form two valves, each bearing seeds alternately on the ventral margin. Dehiscence is due to differential drying of the carpel wall, which in some species may result in explosive release of the seeds. The valves may also twist during dehydration, dislodging any remaining seeds. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pod. A dry many-seeded, dehiscent fruit, such as a legume or a capsule. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pollen
- Pollen. The male germ cells produced in the anthers. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pollen grain
- Pollen grain. In seed-bearing plants, a microspore containing an immature or mature male gametophyte (microgametophyte). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Pollen tube
- Pollen tube. The tube that extends from the pollen grain into the ovule carrying the male gametes to the female gametophyte. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Pollination
- Pollination. In angiosperms, the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. In gymnosperms, the transfer of pollen from the pollen-producing (male) cone to the ovules of the ovulate (female) cone. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Polycarpellary
- Polycarpellary. Seeds derived from a number of fused ovaries. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Pome
- Pome. A type of false fruit, e.g. apple, pear. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Potassium nitrate
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3). A chemical used to increase membrane permeability. In animal research, potassium increases membrane permeability and sodium decreases membrane permeability. The nitrate increases stem elongation and shortens roots. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Prechill
- Prechill. A cold, moist treatment applied to seeds to overcome dormancy prior to the germination test. The prechill method varies among species, but is usually performed by holding imbibed seeds at a low temperature for a specified period of time. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Predry
- Predry. Place the seed in a shallow layer at a temperature of 35°C to 40°C for a period of five to seven days, with provision for circulation of the air. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Primary infection
- Primary infection. Infection caused by disease organisms present and active in the seed and/or seedling itself. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Primary leaf
- Primary leaf. The first leaf of leaves above the cotyledons. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Primary root
- Primary root. The root that develops directly from the hypocotyl of the embryo. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Proliferous
- Proliferous. Bearing vegetative buds or bulblets in the inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Prostrate
- Prostrate. Lying flat on the ground. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Protandry
- Protandry. Anthers of a lower shed their pollen before the stigmas are receptive. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Protogyny
- Protogyny. The stigmas of a flower are receptive before its anthers shed their pollen. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pseudocarp
- Pseudocarp. A false fruit, e.g. pome (apple, pear), strawberry. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pseudocarp. A fruit, such as strawberry, apple or pear, including parts other than the ripened ovary. Also referred to as: false fruit, accessory fruit. TWS
-
Puberulent
- Puberulent. Very short hairs. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Pubescent
- Pubescent. Covered with soft hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pulse
- Pulse. Leguminous plants grown for their edible seeds. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Punctate
- Punctate. Covered with colored dots, or sessile or embedded transparent glands, of minute depressions. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Pure live seed (PLS)
- Pure live seed (PLS). The percentage of pure seeds in a lot that are viable. The basic formula to calculate Pure Live Seed (PLS) is: Percent (%) Pure x Percent (%) Total Viable / 100 = % PLS where (% Total Viable = % Germination + %Hard Seed + %Dormant Seed). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Pure seed unit (PSU) definitions
- Pure seed unit (PSU) definitions. The seed units described in Table 3A shall be considered pure seed. Structures not specifically described as part of the PSU shall be removed and classified as inert matter (refer to section 3.5). Seeds of other species adhering to seed units of the kind under consideration shall be detached and classified as either weed seed or other crop seed (refer to section 4). The PSU numbers given for species in Table 2A correspond to the PSU numbers in Table 3A. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Purity analysis
- Purity analysis. The objective of a purity analysis is to determine the physical composition of the working sample. The analysis shall include the identification of the kind, or kind and cultivar of seed under consideration, and all contaminating species and inert matter. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Purity. The term “purity” means the name or names of the kind, type, or variety and the percentage or percentages thereof; the percentage of other agricultural seed or crop seed; the percentage of weed seeds, including noxious-weeds seeds; the percentage of inert matter; and the names of the noxious-weed seeds and the rate of occurrence of each. Agricultural Marketing Service, USDA. Federal Seed Act, Part 201. Federal Seed Act Regulations. 201.2 Terms Defined. Current as of May 21, 2020.
-
Purity working sample
- Purity working sample. The sub-sample taken from the submitted sample on which the purity analysis is performed. See sections 2.3 b and 3. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Pyramidal
- Pyramidal. Shaped like a pyramid. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Pyrene
- Pyrene. Seed enclosed by the hard endocarp from a drupe (or similar structures from multi-seeded fruits). 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Pyrene, A seed enclosed by the hard endocarp of a drupe, or similar structures from multi-seeded fruits, also kernel or stone (see drupe for illustrations). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Pyrene. The hard, indehiscent, one-seeded portion of a drupe or drupelet (stone or pit). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Pyriform
- Pyriform. Pear-shaped. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
Q
-
Quiescence
- Quiescence. The absence of growth, usually inferring the absence of environmental conditions favoring growth. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
R
-
Raceme
- Raceme. Inflorescence in which the spikelets are pediceled on a rachis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rachilla
- Rachilla, rhachilla. A secondary rachis. In particular in grasses the axis that bears the floret. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Rachilla [pl. rachillae]. A secondary rachis, in grasses: the axis that bears the floret within the spikelet. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Rachilla. The main axis of a grass or sedge spikelet. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Rachilla. The axis of a spikelet. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rachis
- Rachis, rhachis [pl. rachides]. The main axis of an inflorescence. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Rachis. The main axis of an inflorescence (or compound leaf). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Rachis. The axis of a spike or raceme. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rachis segment
- Rachis segment. In grasses: a segment of the rachis that remains attached to a spikelet. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Radical
Springing from the root; clustered at the base of the stem. -
Radical
- Radical. The lower portion of the hypocotyl which grows into the primary root. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Radicle
- Radicle. The initial root of the embryo, which develops into the primary root after emergence through the testa during germination. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Radicle
The part of an embryo giving rise to the root system of a plant. Compare to plumule. -
Rame
- Rame. A disarticulating inflorescence branch that forms the basic unit of a typical Andropogoneae inflorescence. [Refer to Barkworth, M. E., K. M. Capels, S. Long, and M. B. Piep. 2003. Flora of North America, Volume 25, Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in part): Poaceae, part 2. Oxford University Press. 783 pp.] Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Rame internode
- Rame internode. A segment of an inflorescence branch in the Andropogoneae. (Note: the dispersal unit usually consists of a spikelet pair and a rame internode that extends from the sessile spikelet to the next most distal sessile spikelet. In Tripsacum, a single spikelet is present in each pistillate segment of the proximal portion of the inflorescence branch while pairs of staminate spikelets are present in the distal portion of the inflorescence branch. Also see rame.) Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Raphe
- Raphe. A ridge in seeds formed by the fusion of the seed stalk and the testa. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Ray
- Ray. Corolla of a marginal flower of a composite inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Recalcitrant
- Recalcitrant. Desiccation sensitive. Not able to survive drying to low moisture contents. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020
-
Receptacle
- Receptacle. Apex of a pedicel or peduncle from which the organs of a flower arise. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Recurved
- Recurved. Bent backwards. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Reflexed
- Reflexed. A part bent back upon itself. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Reniform
- Reniform. Kidney-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Respiration
- Respiration. The metabolic process by which an organism takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide and other products of oxidation. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Reticulate
- Reticulate. In the form of a network. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Reticulation
- Reticulation. A raised surface area resembling a network of mesh. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Retrorse
- Retrorse. Pointed backward or downward. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rhizomatous
- Rhizomatous. Having rhizomes or appearing like rhizomes, as the base of a decumbent stem. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rhizome
- Rhizome. A horizontal underground stem from which shoots and adventitious roots may arise at the nodes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rigid
- Rigid. Stiff, not flexible. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Root
- Root. In dicotyledons and gymnosperms, the root system serves three major functions: (1) to anchor the plant in the soil, (2) to absorb water and dissolved salts from the soil and (3) to conduct the water and salts to the hypocotyl, cotyledons and epicotyl. The embryonic root, or radicle, is located at the basal end of the embryo and is usually the first seedling structure to rupture the testa. After emergence it is referred to as the primary root. The primary root elongates rapidly and soon numerous root hairs develop, greatly increasing the absorbing surface of the roots. As the seedling continues to grow, secondary roots develop from the primary root and from other secondary roots. Roots may also emerge from other structures (e.g. the hypocotyl) and are referred to as adventitious roots. As in the dicotyledons, the monocotyledon root system serves to anchor the plant in soil, absorb water and dissolved salts from the soil and to conduct the water and salts to the growing seedling. The embryonic root, or radicle, is situated at the basal end of the embryo and, in the case of the Poaceae, its apex is covered by the coleorhiza. After the radicle emerges it is referred to as the primary root. In some species of the Poaceae (e.g. Triticum) the primary root is indistinguishable from the other roots that develop from the scutellar node region and hence all of these are referred to as seminal roots. Roots that develop from structures above the scutellar or cotyledonary node are called adventitious roots. Secondary roots may develop from seminal and adventitious roots. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Root. A portion of a higher plant bearing neither leaves nor reproductive organs, usually underground. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Root hair
- Root hair. Fine tubular growth from an epidermal cell of a root. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Root tip
Root tips will grow into tap roots or fibrous roots. A root tip is protected by a root cap. Within a root tip, cell: differentiation, actively dividing and increasing in length, depending on the zone of the root tip. -
Rootstock
- Rootstock. A rhizome. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rosette
- Rosette. A cluster of spreading or radiating basal leaves. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rudimentary
- Rudimentary. Imperfectly developed. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Rudimentary embryos
- Rudimentary embryos. Embryos that are small, immature and sometimes undifferentiated at the time of seed release from the parent plant. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Rugose
- Rugose. Wrinkled. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Runner
- Runner. A prostrate, slender, above-ground stem or stolon. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
S
-
Saccate
- Saccate. Sack-shaped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sagittate
- Sagittate. Shaped like an arrow-head. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Samara
- Samara. An indehiscent, winged fruit; a type of achene with a pericarp extended into a membranous wing to aid wind dispersal of the seed, e.g. the winged fruits or keys of Fraxinus excelsior. The double samara typical of Acer is a kind of schizocarp. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Samara. A dry, indehiscent fruit, with a wing-like extension of the pericarp. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Sarcotesta
- Sarcotesta. A fleshy seed coat. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Scabrous
- Scabrous. Rough to the touch. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Scale
- Scale. Reduced leaves at the base of a shoot. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Scale leaf
- Scale leaf. A reduced leaf, usually appressed to the stem (e.g. in Asparagus, Pisum). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Scarification
- Scarification. The process of mechanically or chemically abrading a seed coat to make it more permeable to water and gases. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Scarious
- Scarious. Thin, dry, membranaceous, not green. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Schizocarp
- Schizocarp. A dry fruit which separates into two or more units (mericarps) at maturity. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Schizocarp. A dry fruit which separates into two or more single seeded units (mericarps) at maturity, e.g. in Apiaceae. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Schizocarp. A dry fruit that splits into one-seeded segments (mericarps) at maturity. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Scutellum
- Scutellum. Shield-shaped organ surrounding the embryo of a grass that is morphologically like a cotyledon. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Secondary dormancy
- Secondary dormancy. A type of dormancy imposed by certain adverse environmental conditions in previously nondormant seeds, or seeds in which primary dormancy has been broken. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Secondary infection
- Secondary infection. Infection caused by disease organisms spreading from other seeds or seedlings or adhering structures (e.g. the cluster of Beta). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Secund
- Secund. One-sided or arranged along one side. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Seed
- Seed. The part of a plant which is able to develop into a new plant. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Seed. Botanically, a seed is a mature fertilized ovule containing an embryonic plant; usually it has nutrient storage tissue and is surrounded by a protective coat, the testa. This structure is a "true seed"; however, the ovules of many species have additional structures of the mother plant attached or fused to the seed coat. For example, the "seed" of Triticum aestivum (wheat) is botanically a fruit because the pericarp (ovary wall) is fused with the seed coat. In these rules the term "seed" will be used in the agronomic sense (i.e. the true seed plus any accessory structures that may be attached when it is planted in the field; see section 3.2 of the AOSA Rules for Testing Seeds Vol. 1). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
- Seed. The ripened ovule, enclosing the rudimentary plant and food necessary for its germination. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Seed blower
- Seed blower. A mechanical device utilizing a vertical air stream in a tube to aid in the separation of components in a seed sample. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Seed coverings
- Seed coverings. Accessory structures such as bracts, fruit walls, and floral parts. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Seed herbarium
- Seed herbarium. A reference collection of validated and preserved seeds, fruits and other propagules used for scientific study or seed identification. TWS
-
Seed lot
- Seed lot. A seed lot is a specified quantity of seed that is physically and uniquely identified. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing, (ISTA)
- Lot of seed. The term "lot of seed" means a definite quantity of seed identified by a number, every portion or bag which is uniform, within permitted tolerances, for the factors which appear in the labeling. Agricultural Marketing Service, USDA. Federal Seed Act, Part 201. Federal Seed Act Regulations. 201.2 Terms Defined. Current as of May 21, 2020.
-
Seed moisture determination working sample
- Seed moisture determination working sample. The sub-sample taken from the submitted sample on which the seed moisture determination is performed. See sections 2.3 e and 11. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Seed unit
- Seed unit. Commonly found dispersal unit, i.e. achenes and similar fruits, schizocarps, florets etc., as defined for each genus or species in the Pure Seed Definitions in Table 3B Parts 1 and 2. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
-
Seed unit
- Seed unit. Commonly found dispersal unit, i.e. achenes and similar fruits, schizocarps, florets etc., as defined for each genus or species in the ISTA Rules, Table 3B Parts 1 & 2. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Seed unit. The structure usually regarded as a seed in planting practices and in commercial channels. Refer to section 3.2 e for pure seed unit definitions. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Seed vigor
- Seed vigor. Those seed properties that determine the potential for rapid, uniform emergence and development of normal seedlings under a wide range of field conditions. AOSA Seed Vigor Handbook, 2009
-
Seedling
- Seedling. A young plant developing from the embryo of a seed. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Self-pollinated
- Self-pollinated. Pollinated by pollen from the same plant. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Seminal
- Seminal. Relating to the seed. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Seminal roots
- Seminal roots. Roots that arise from the embryo. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Sepal
- Sepal. A leaf or division of the calyx. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Septum
- Septum. A partition or wall. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Septum. Partition or dividing wall separating two cavities. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Serrate
- Serrate. Saw-toothed. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sessile
- Sessile. Without a stalk or pedicel. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Sessile. Attached directly by the base and not raised on a stalk. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Setaceus
- Setaceus. Bristle-like. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sheath
- Sheath. The lower part of the leaf that encloses the stem, as in grasses. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Shoot
- Shoot. A stem with its attached members. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Shoot apex
- Shoot apex. The terminal portion of the shoot, containing the main growing point. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Silicula
- Silicula. A dry dehiscent fruit, derived from two carpels fused to form a flattened pod with two loculi separated by a false septum. The seeds are exposed on the septum as the two valves separate from it, from the base up. They are as broad as or broader than they are long (e.g. Capsella bursa-pastoris). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Siliqua
- Siliqua. Dehiscent, dry, two-valved fruit derived from two carpels, e.g. Brassicaceae. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Siliqua. A dry, dehiscent, two-valved fruit derived from two carpels, similar to a silicula but long and narrow. It is typical of Brassica. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Simple fruit
- Simple fruit. A fruit which develops from the gynoecium of a single flower (=true fruit). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Sinus
- Sinus. A depression or notch in a margin between two lobes. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Soil/Riffle divider
- Soil/Riffle divider. This divider consists of a hopper with attached channels or ducts, a frame to hold the hopper, four collection containers and a pouring pan. Ducts or channels lead from the hopper to the collection containers, alternate ones leading to opposite sides. Riffle dividers are available in different sizes for different sizes of seed. The width and number of channels and spaces are important. The minimum width of the channels must be at least two times the largest diameter of the seed or any possible contaminants being mixed. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Spathe
- Spathe. A sheathing bract of the inflorescence. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Species
- Species. A category of classification lower than a genus that is made up of plants which possess in common distinctive characteristics that are reproduced in their offspring. The species name included second to the genus in the scientific binomial. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Spike
- Spike. An unbranched inflorescence in which the spikelets are sessile on a rachis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Spikelet
- Spikelet. The unit of a grass inflorescence comprising one or more florets subtended by one or two sterile glumes. For the purposes of the Rules, the term spikelet includes, as well as a fertile floret, either one or more additional fertile or completely infertile florets, or glumes. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Spikelet. Part of a grass inflorescence including one or more florets subtended by one or two glumes. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Spikelet. In grasses: One or more attached florets usually subtended by one or more bracts (glumes). Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Spikelet. The unit of a grass inflorescence that consists of a pair of empty glumes that enclose one of more florets arranged around a rachilla. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Spindly
- Spindly. Disproportionately thin relative to length; thread-like in appearance. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Spreading
- Spreading. Having an outward direction. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Squarrose
- Squarrose. Spreading or recurved at the tip. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stalk
- Stalk. The stem of any plant organ. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
-
Stamen
- Stamen. The male sex organ of a flower, including the filament and anther. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Stamen.The pollen-bearing organs of a flower. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Staminate
-
Staminate floret
- Staminate floret. A floret bearing stamens only, with no functional ovary. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Standard
- Standard. The large upper petal of a papilionaceous corolla, as in some legumes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sterile
- Sterile. Without functional sex organs (for grass florets: without caryopsis). 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Sterile. Without pistils. A sterile floret may be staminate or neuter. It may even lack a palea, and consist of nothing but a lemma. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sterile floret
- Sterile floret. A floret with no caryopsis. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Sterile lemma
- Sterile lemma. In a single-seeded grass spikelet: a lemma which does not enclose a caryopsis. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Stigma
- Stigma. The pollen-trapping part of a pistil. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Stigma. The part of the pistil receptive to pollen grains. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stipe
- Stipe. A minute stalk to an organ. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stipitate
- Stipitate. Having a stipe. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stipule
- Stipule. One of the pair of appendages borne at the base of the petiole. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stock
- Stock. The main stem of a plant; sometimes referred to as a stalk. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stolon
- Stolon. A modified propagating creeping stem above ground. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Stomata
- Stomata. Pores or apertures, surrounded by two guard cells, which allow gaseous exchange. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Stone
- Stone. In a drupe, the hardened endocarp containing a kernel. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
Stooling
- Stooling. Production of secondary branches from lowermost nodes, as in grasses; tillering. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Storage tissue
- Storage tissue. The storage tissue in seeds may originate from four sources depending on the species: (1) perisperm; (2) endosperm; (3) cotyledons and (4) female gametophyte. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Stractification
- Stratification. A method of overcoming seed dormancy; seeds are placed in a moist medium and exposed to either cold or warm temperatures, depending on the required treatment for the species involved. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Stramineus
- Stramineus. Straw-colored. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Striate
- Striate. Marked with parallel lines or ridges. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Strigose
- Strigose. Rough with short, stiff hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Strophiole
-
Stubby root
- Stubby root. Blunt, broken off or dwarfed. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Style
- Style. The slender stalk that bears the stigma. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Style. The slender part of the pistil supporting the stigma. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Subtend
- Subtend. To enclose from below, as a bract subtends a branch in its axil. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Subtend
To stand beneath or close to, such as a bract at the base of a flower. -
Subulate
- Subulate. Linear and tapering to a fine point. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Succulent
- Succulent. Fruits in which the mesocarp develops into a fleshy covering. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Succulent. Fleshy or juicy. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sucker
- Sucker. A shoot produced from the crown or a rhizome; a tiller. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Sulcate
- Sulcate. Furrowed or grooved. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Super Chaffy Seed
- Super chaffy seed. Seed units that tangle with other seed units or inert matter and adhere to other seed units or other surfaces because of their structure or texture, or kinds of seed that are difficult to clean and condition because of their fragile structures, thus making it only possible to sample a seed lot using the hand method and difficult to mix and divide a representative working sample using a mechanical divider. This definition is not applicable to coated, pelleted, encrusted, or hulled seeds that are normally classified as super-chaffy whether as a single kind under consideration or as components of seed mixtures. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Suture
- Suture. A seam or line of union. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Swollen seeds
- Swollen seeds. Seeds which have imbibed water, but which do not show radicle or shoot protrusion. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
T
-
Taproot
- Taproot. The primary root, distinctly larger and more conspicuous than any of its branches. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Tassel
- Tassel. Staminate inflorescence, as in corn. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Teeth
- Teeth. Pointed lobes or divisions. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Tendril
- Tendril. A leaflet or stem modified for climbing or anchorage. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Terete
- Terete. Cylindrical and slender. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Terminal
- Terminal. Extremity or upper bud, flower, or leaf. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Terminal bud
- Terminal bud. The shoot apex enveloped by several more or less differentiated leaves. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Terminal bud. The terminal bud occupies the tip of the epicotyl and consists of the apical meristem surrounded and protected by the developing leaves. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 4, 2019
-
Testa
-
Tillering
- Tillering. Production of branches from the lowermost nodes or crown, as in grasses. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Tomentose
- Tomentose. Covered with densely matted hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Total viability
- Total viability. The sum of percentage germination plus dormant plus hard seeds. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Trailing
- Trailing. Prostrate on the ground. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Translucent
- Translucent. Permits some passage of light, but diffuses it. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Transversely
Cutting from side to side. -
Trichome
- Trichome. Any epidermal hair structure in plants. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Trifoliate
- Trifoliate. Leaf blade with three leaflets. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
True fruit
- True fruit. A fruit which develops from the gynoecium of a single flower (=simple fruit). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
-
True seed
- True seed. A mature fertilized ovule consisting of an embryo, with or without an external food reserve (e.g. endosperm) enclosed by the testa. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Truncate
- Truncate. Having the end square or even. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Tufted
- Tufted. Clustered in branches; clumped. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Turgid
- Turgid. Swollen. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Tussock
- Tussock. A dense tuft or bunch of grass. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Two-ranked
- Two-ranked. Having two ranks, distichous. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
U
-
Umbel
- Umbel. An inflorescence with the pedicels arising from the same point. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Undulate
- Undulate. Having a wavy surface. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Uniform blowing procedure
- Uniform blowing procedure. A standard purity procedure required for certain grass species that separates pure seed units from inert material using a seed blower. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Uniform Classification of Weed and Crop Seeds
- Uniform Classification of Weed and Crop Seeds. For classification of weed and crop seeds, refer to the AOSA Rules for Testing Seeds Volume 3. Uniform Classification of Weed and Crop Seeds, AOSA 2009, and subsequent updates. This entire volume shall be considered part of the Rules and its use is required for determination of classification of the kind of seed under consideration and classification of weed and crop seed contaminants for purity testing. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
-
Unilateral
- Unilateral. Produced or arranged on one side. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Utricle
- Utricle. A dry, thin-walled, one-seeded, bladder-like fruit. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
V
-
Valve
- Valve. One of the sections of a capsule. ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Valve. One of the segments or pieces into which a dehiscing capsule or legume separates. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Variety
- Variety. A group of plants related by descent but distinguished from other similar groups by characters too trivial to entitle it to recognition as a species. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Vascular tissues
- Vascular tissues. Seed conducting tissues (consisting of phloem and xylem where water and nutrients move throughout the plant). SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Vein
- Vein. A bundle of threads of fibro-vascular tissue in a leaf or other organ. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Veins
- Veins. Strands of vascular tissue visible from the surface of plant structures. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Venation
- Venation. The arrangement of veins. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Venticillate
- Venticillate. Arranged in whorls. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Ventral
- Ventral. The side facing towards the axis; the lower surface (dorsal). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Ventral. The lower or front side; opposite to dorsal. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Vernal
- Vernal. Pertains to, appears or occurs, in the spring. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Vernation
- Vernation. The arrangement of leaves in a bud. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Vestigial
- Vestigial. A small, imperfectly developed part. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Viable (viability)
- Viable [viability]. Alive. Seed viability indicates that a seed contains structures and substances including enzyme systems that give it the capacity to germinate under favorable conditions in the absence of dormancy. SCST Seed Technologist Training Manual, 2018
-
Villous
- Villous. Bearing long, soft, straight hairs. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
W
-
Water potential
Water potential. The potential energy of water in a solution compared to pure water. A water potential measurement gives an indication of the availability of water in a solution. Bowden, L., Moisture Testing in Wild Species. TWS Website. 2020 -
Web
- Web. The cluster of slender, soft hairs at the base of the floret, as in certain species of Poa. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Weed seed
- Weed seed. Seeds, florets, bulblets, tubers, or sporocarps of plants recognized as weeds by laws, official regulations, or by general usage shall be considered weed seeds; refer to section 4. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 1, 2019
- Weeds. Undesirable species that are excessively competitive, difficult to control or eradicate, poisonous, or simply not wanted. Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) Rules for Seed Testing, Volume 3, 2019
-
Whorl
- Whorl. Arranged in a circle around an axis. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111
-
Wing
- Wing. A flat membranous outgrowth from a fruit or seed. 2020 International Rules for Seed Testing (ISTA)
- Wing. A flat membranous outgrowth from a fruit or seed (e.g. Coreopsis, Dimorphotheca). ISTA Handbook on Pure Seed Definitions, Glossary. 3rd Edition 2010
- Wing. Lateral petal of a papilionaceous corolla, as in some legumes. Fenwick, J.R. revised 1995. Laboratory Manual for General Crops- Glossary. Unpublished class notes. Dept. of Soil and Crop Sciences, Colorado State University. Pages 104-111